Page 125 - Wire Bonding in Microelectronics
P. 125
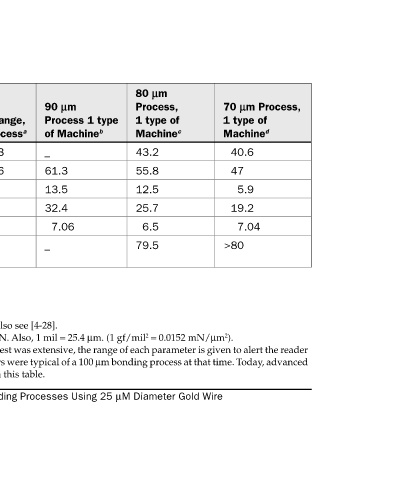
lm Process,
70 1 type of Machine d 40.6 47 5.9 19.2 7.04 >80
lm Process, 1 type of Machine c 6.5
80 43.2 55.8 12.5 25.7 79.5
Process 1 type
lm of Machine b 7.06
90 _ 61.3 13.5 32.4 _
Observed Range, lm Process a 100 45.4 to 56.3 67.7 to 78.6 12 to 17.2 27.2 to 43 3.7 to 6.4 79.6 to 47 e Milli-Newton (mN) units may be substituted for grams-force (gf), 1 gf = 9.8 mN. Also, 1 mil = 25.4 µm. (1 gf/mil 2 = 0.0152 mN/µm 2 ). Note: Data in table (4-3) were summarized
lm Avg. of 5 Machine a
100 50 74 16.1 35.4 5.36 65.6 a Five Different Mfg. Machines, (averaged) data obtained over 8 h runs [4-26]. d K&S and SEMATECH, Several Identical Machines (private communication) Also see [4-28]. bonders can produce much finer pitch and closer tolerances than indicated in this table
Machine or Test Parameter Free-Air Ball Dia. (µm) Bonded Ball Dia. (µm) Bonded Ball Height (µm) Shear Force (gf) Shear Strength (gf/mil 2 ) e Intermetallics Under Ball (% interface area) b One Type of Machine [4-26]. c ESEC, Several Identical Machines [4-27].
TABLE 4-1
103