Page 127 - Wire Bonding in Microelectronics
P. 127
W ir e Bond Testing 105
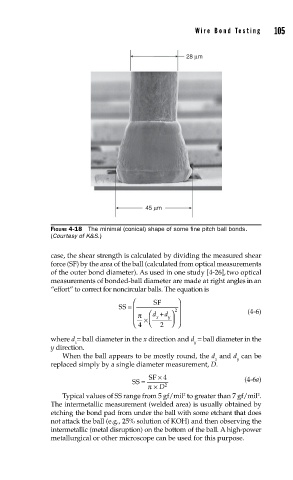
28 µm
45 µm
FIGURE 4-18 The minimal (conical) shape of some fi ne pitch ball bonds.
(Courtesy of K&S.)
case, the shear strength is calculated by dividing the measured shear
force (SF) by the area of the ball (calculated from optical measurements
of the outer bond diameter). As used in one study [4-26], two optical
measurements of bonded-ball diameter are made at right angles in an
“effort” to correct for noncircular balls. The equation is
SF
SS = 2
π × d x +d y (4-6)
4 2
where d = ball diameter in the x direction and d = ball diameter in the
x y
y direction.
When the ball appears to be mostly round, the d and d can be
x y
replaced simply by a single diameter measurement, D.
SS = SF × 4 (4-6a)
π × D 2
2
Typical values of SS range from 5 gf/mil to greater than 7 gf/mil .
2
The intermetallic measurement (welded area) is usually obtained by
etching the bond pad from under the ball with some etchant that does
not attack the ball (e.g., 25% solution of KOH) and then observing the
intermetallic (metal disruption) on the bottom of the ball. A high-power
metallurgical or other microscope can be used for this purpose.