Page 67 - Wire Bonding in Microelectronics
P. 67
46 Cha pte r T w o
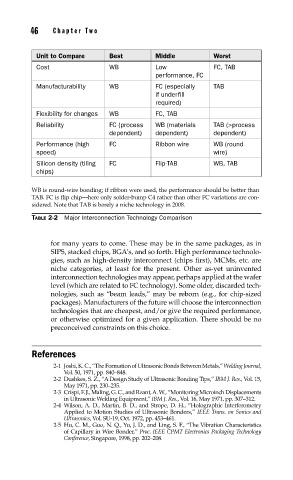
Unit to Compare Best Middle Worst
Cost WB Low FC, TAB
performance, FC
Manufacturability WB FC (especially TAB
if underfill
required)
Flexibility for changes WB FC, TAB
Reliability FC (process WB (materials TAB (>process
dependent) dependent) dependent)
Performance (high FC Ribbon wire WB (round
speed) wire)
Silicon density (tiling FC Flip-TAB WB, TAB
chips)
WB is round-wire bonding; if ribbon were used, the performance should be better than
TAB. FC is flip chip—here only solder-bump C4 rather than other FC variations are con-
sidered. Note that TAB is barely a niche technology in 2008.
TABLE 2-2 Major Interconnection Technology Comparison
for many years to come. These may be in the same packages, as in
SIPS, stacked chips, BGA’s, and so forth. High performance technolo-
gies, such as high-density interconnect (chips first), MCMs, etc. are
niche categories, at least for the present. Other as-yet uninvented
interconnection technologies may appear, perhaps applied at the wafer
level (which are related to FC technology). Some older, discarded tech-
nologies, such as “beam leads,” may be reborn (e.g., for chip-sized
packages). Manufacturers of the future will choose the interconnection
technologies that are cheapest, and/or give the required performance,
or otherwise optimized for a given application. There should be no
preconceived constraints on this choice.
References
2-1 Joshi, K. C., “The Formation of Ultrasonic Bonds Between Metals,” Welding Journal,
Vol. 50, 1971, pp. 840–848.
2-2 Dushkes, S. Z., “A Design Study of Ultrasonic Bonding Tips,” IBM J. Res., Vol. 15,
May 1971, pp. 230–235.
2-3 Crispi, F. J., Maling, G. C., and Rzant, A. W., “Monitoring Microinch Displacements
in Ultrasonic Welding Equipment,” IBM J. Res., Vol. 16, May 1971, pp. 307–312.
2-4 Wilson, A. D., Martin, B. D., and Strope, D. H., “Holographic Interferometry
Applied to Motion Studies of Ultrasonic Bonders,” IEEE Trans. on Sonics and
Ultrasonics, Vol. SU-19, Oct. 1972, pp. 453–461.
2-5 Hu, C. M., Guo, N. Q., Yu, J. D., and Ling, S. F., “The Vibration Characteristics
of Capillary in Wire Bonder,” Proc. IEEE CPMT Electronics Packaging Technology
Conference, Singapore, 1998, pp. 202–208.