Page 335 - Characterization and Properties of Petroleum Fractions - M.R. Riazi
P. 335
P2: IML/FFX
QC: IML/FFX
P1: IML/FFX
AT029-Manual
June 22, 2007
AT029-07
AT029-Manual-v7.cls
7. APPLICATIONS: ESTIMATION OF THERMOPHYSICAL PROPERTIES 315
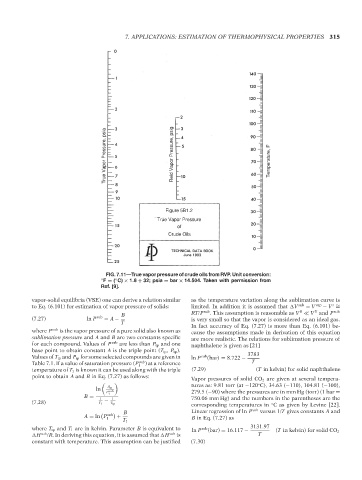
True Vapor Pressure, psia T1: IML 17:40 Reid Vapor Pressure, psig Temperature, F
Figure 5B1.2
True Vapor Pressure
of
Crude Oils
FIG. 7.11—True vapor pressure of crude oils from RVP. Unit conversion:
◦
◦ F = ( C) × 1.8 + 32; psia = bar × 14.504. Taken with permission from
Ref. [9].
vapor–solid equilibria (VSE) one can derive a relation similar as the temperature variation along the sublimation curve is
to Eq. (6.101) for estimation of vapor pressure of solids: limited. In addition it is assumed that V sub = V vap − V =
s ∼
S
V
B RT/P sub . This assumption is reasonable as V V and P sub
(7.27) ln P sub = A − is very small so that the vapor is considered as an ideal gas.
T
In fact accuracy of Eq. (7.27) is more than Eq. (6.101) be-
where P sub is the vapor pressure of a pure solid also known as cause the assumptions made in derivation of this equation
sublimation pressure and A and B are two constants specific are more realistic. The relations for sublimation pressure of
for each compound. Values of P sub are less than P tp and one naphthalene is given as [21]
base point to obtain constant A is the triple point (T tp , P tp ).
Values of T tp and P tp for some selected compounds are given in ln P sub (bar) = 8.722 − 3783
Table 7.1. If a value of saturation pressure (P 1 sub ) at a reference T
temperature of T 1 is known it can be used along with the triple (7.29) (T in kelvin) for solid naphthalene
point to obtain A and B in Eq. (7.27) as follows: Vapor pressures of solid CO 2 are given at several tempera-
tures as: 9.81 torr (at −120 C), 34.63 (−110), 104.81 (−100),
◦
ln P tp
P sub 279.5 (−90) where the pressures are in mm Hg (torr) (1 bar =
1
B = 1 1 750.06 mm Hg) and the numbers in the parentheses are the
(7.28) T 1 − T tp
corresponding temperatures in C as given by Levine [22].
◦
B Linear regression of ln P sub versus 1/T gives constants A and
A = ln P 1 sub + B in Eq. (7.27) as
T 1
where T tp and T 1 are in kelvin. Parameter B is equivalent to ln P sub (bar) = 16.117 − 3131.97 (T in kelvin) for solid CO 2
H sub /R. In deriving this equation, it is assumed that H sub is T
constant with temperature. This assumption can be justified (7.30)
--`,```,`,``````,`,````,```,,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
Copyright ASTM International
Provided by IHS Markit under license with ASTM Licensee=International Dealers Demo/2222333001, User=Anggiansah, Erick
No reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS Not for Resale, 08/26/2021 21:56:35 MDT