Page 401 - Characterization and Properties of Petroleum Fractions - M.R. Riazi
P. 401
P2: IML/FFX
T1: IML
QC: IML/FFX
P1: IML/FFX
June 22, 2007
AT029-Manual-v7.cls
14:25
AT029-09
AT029-Manual
99.4
70.0
( a ) 9. APPLICATIONS: PHASE EQUILIBRIUM CALCULATIONS 381
( b )
65.0
99.3
Percent of asphaltene precipitated 99.2 Percent of asphaltene precipitated 60.0
55.0
99.1
99.0
50.0
98.9
98.8 45.0
40.0
270 280 290 300 310 320 330 340 350 360 240 250 260 270 280 290 300 310 320
T, K T, K
(a) (b)
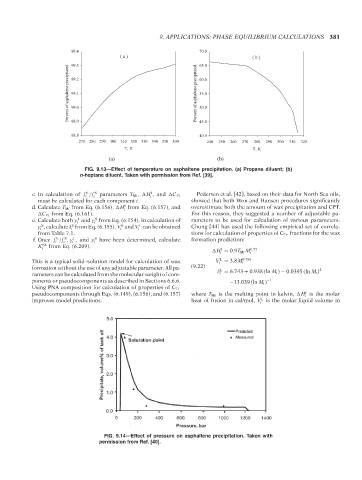
FIG. 9.13—Effect of temperature on asphaltene precipitation. (a) Propane diluent; (b)
n-heptane diluent. Taken with permission from Ref. [39].
c. In calculation of f /f i S parameters T Mi , H , and C Pi Pedersen et al. [42], based on their data for North Sea oils,
L
f
i
i
must be calculated for each component i. showed that both Won and Hansen procedures significantly
f
d. Calculate T Mi from Eq. (6.156), H from Eq. (6.157), and overestimate both the amount of wax precipitation and CPT.
i
C Pi from Eq. (6.161). For this reason, they suggested a number of adjustable pa-
L
S
e. Calculate both γ and γ from Eq. (6.154). In calculation of rameters to be used for calculation of various parameters.
i
i
S
S
L
S
γ , calculate δ from Eq. (6.155). V and V can be obtained Chung [44] has used the following empirical set of correla-
i
i
i
i
from Table 7.1. tions for calculation of properties of C 7+ fractions for the wax
L
S
L
f. Once f /f , γ , and γ i S have been determined, calculate formation prediction:
i
i
i
K SL from Eq. (6.209).
i f 0.55
H = 0.9T Mi M i
i
L
This is a typical solid–solution model for calculation of wax V = 3.8M 0.786
i
i
formation without the use of any adjustable parameter. All pa- (9.22) L 2
rameters can be calculated from the molecular weight of com- δ = 6.743 + 0.938 (ln M i) − 0.0395 (ln M i)
i
ponents or pseudocomponents as described in Sections 6.6.6. −13.039 (ln M i) −1
Using PNA composition for calculation of properties of C 7+
f
pseudocomponents through Eqs. (6.149), (6.156), and (6.157) where T Mi is the melting point in kelvin, H is the molar
i
L
improves model predictions. heat of fusion in cal/mol, V is the molar liquid volume in
i
FIG. 9.14—Effect of pressure on asphaltene precipitation. Taken with
permission from Ref. [40].
Copyright ASTM International
Provided by IHS Markit under license with ASTM Licensee=International Dealers Demo/2222333001, User=Anggiansah, Erick
No reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS Not for Resale, 08/26/2021 21:56:35 MDT
--`,```,`,``````,`,````,```,,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---