Page 86 - Petroleum Production Engineering, A Computer-Assisted Approach
P. 86
Guo, Boyun / Computer Assited Petroleum Production Engg 0750682701_chap06 Final Proof page 78 3.1.2007 8:40pm Compositor Name: SJoearun
6/78 PETROLEUM PRODUCTION ENGINEERING FUNDAMENTALS
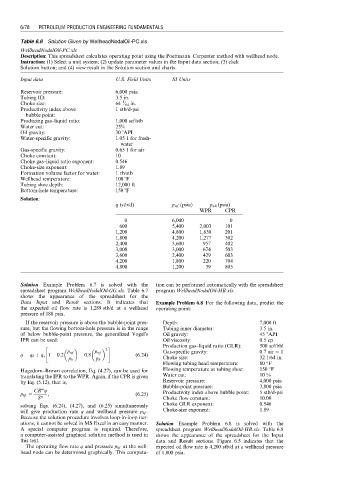
Table 6.6 Solution Given by WellheadNodalOil-PC.xls
WellheadNodalOil-PC.xls
Description: This spreadsheet calculates operating point using the Poettmann–Carpenter method with wellhead node.
Instruction: (1) Select a unit system; (2) update parameter values in the Input data section; (3) click
Solution button; and (4) view result in the Solution section and charts.
Input data U.S. Field Units SI Units
Reservoir pressure: 6,000 psia
Tubing ID: 3.5 in.
1
Choke size: 64 ⁄ 64 in.
Productivity index above 1 stb/d-psi
bubble point:
Producing gas–liquid ratio: 1,000 scf/stb
Water cut: 25%
Oil gravity: 30 8API
Water-specific gravity: 1.05 1 for fresh-
water
Gas-specific gravity: 0.65 1 for air
Choke constant: 10
Choke gas–liquid ratio exponent: 0.546
Choke-size exponent: 1.89
Formation volume factor for water: 1 rb/stb
Wellhead temperature: 100 8F
Tubing shoe depth: 12,000 ft
Bottom-hole temperature: 150 8F
Solution:
q (stb/d) p wf ðpsiaÞ p wh (psia)
WPR CPR
0 6,000 0
600 5,400 2,003 101
1,200 4,800 1,630 201
1,800 4,200 1,277 302
2,400 3,600 957 402
3,000 3,000 674 503
3,600 2,400 429 603
4,200 1,800 220 704
4,800 1,200 39 805
Solution Example Problem 6.7 is solved with the tion can be performed automatically with the spreadsheet
spreadsheet program WellheadNodalOil-GG.xls. Table 6.7 program WellheadNodalOil-HB.xls.
shows the appearance of the spreadsheet for the
Data Input and Result sections. It indicates that Example Problem 6.8 For the following data, predict the
the expected oil flow rate is 1,289 stb/d at a wellhead operating point:
pressure of 188 psia.
If the reservoir pressure is above the bubble-point pres- Depth: 7,000 ft
sure, but the flowing bottom-hole pressure is in the range Tubing inner diameter: 3.5 in.
of below bubble-point pressure, the generalized Vogel’s Oil gravity: 45 8API
IPR can be used: Oil viscosity: 0.5 cp
" 2 # Production gas–liquid ratio (GLR): 500 scf/bbl
p wf p wf Gas-specific gravity: 0.7 air ¼ 1
q ¼ q b þ q v 1 0:2 0:8 (6:24) Choke size: 32 1/64 in.
p b p b
Flowing tubing head temperature: 80 8F
Hagedorn–Brown correlation, Eq. (4.27), can be used for Flowing temperature at tubing shoe: 150 8F
translating the IPR to the WPR. Again, if the CPR is given Water cut: 10 %
by Eq. (5.12), that is, Reservoir pressure: 4,000 psia
Bubble-point pressure: 3,800 psia
m
CR q
p hf ¼ , (6:25) Productivity index above bubble point: 5 stb/d-psi
S n Choke flow constant: 10.00
solving Eqs. (6.24), (4.27), and (6.25) simultaneously Choke GLR exponent: 0.546
will give production rate q and wellhead pressure p hf . Choke-size exponent: 1.89
Because the solution procedure involves loop-in-loop iter-
ations, it cannot be solved in MS Excel in an easy manner. Solution Example Problem 6.8 is solved with the
A special computer program is required. Therefore, spreadsheet program WellheadNodalOil-HB.xls.Table 6.8
a computer-assisted graphical solution method is used in shows the appearance of the spreadsheet for the Input
this text. data and Result sections. Figure 6.5 indicates that the
The operating flow rate q and pressure p hf at the well- expected oil flow rate is 4,200 stb/d at a wellhead pressure
head node can be determined graphically. This computa- of 1,800 psia.