Page 185 - A Comprehensive Guide to Solar Energy Systems
P. 185
Chapter 9 • Crystalline Silicon Solar Cell and Module Technology 187
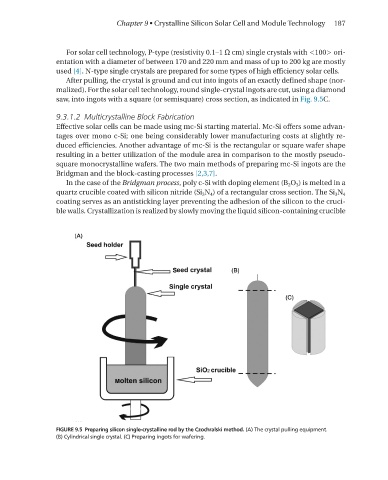
For solar cell technology, P-type (resistivity 0.1–1 Ω cm) single crystals with <100> ori-
entation with a diameter of between 170 and 220 mm and mass of up to 200 kg are mostly
used [4]. n-type single crystals are prepared for some types of high efficiency solar cells.
After pulling, the crystal is ground and cut into ingots of an exactly defined shape (nor-
malized). For the solar cell technology, round single-crystal ingots are cut, using a diamond
saw, into ingots with a square (or semisquare) cross section, as indicated in Fig. 9.5C.
9.3.1.2 Multicrystalline Block Fabrication
effective solar cells can be made using mc-Si starting material. mc-Si offers some advan-
tages over mono c-Si; one being considerably lower manufacturing costs at slightly re-
duced efficiencies. Another advantage of mc-Si is the rectangular or square wafer shape
resulting in a better utilization of the module area in comparison to the mostly pseudo-
square monocrystalline wafers. The two main methods of preparing mc-Si ingots are the
Bridgman and the block-casting processes [2,3,7].
In the case of the Bridgman process, poly c-Si with doping element (B 2 O 3 ) is melted in a
quartz crucible coated with silicon nitride (Si 3 n 4 ) of a rectangular cross section. The Si 3 n 4
coating serves as an antisticking layer preventing the adhesion of the silicon to the cruci-
ble walls. Crystallization is realized by slowly moving the liquid silicon-containing crucible
FIGURE 9.5 Preparing silicon single-crystalline rod by the Czochralski method. (A) The crystal pulling equipment.
(B) Cylindrical single crystal. (C) Preparing ingots for wafering.