Page 310 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 310
5.9 f-k DIP FILTERS 301
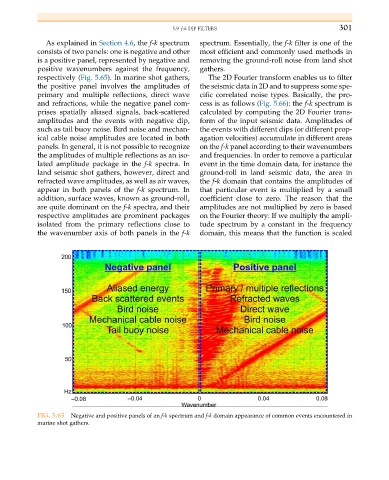
As explained in Section 4.6, the f-k spectrum spectrum. Essentially, the f-k filter is one of the
consists of two panels: one is negative and other most efficient and commonly used methods in
is a positive panel, represented by negative and removing the ground-roll noise from land shot
positive wavenumbers against the frequency, gathers.
respectively (Fig. 5.65). In marine shot gathers, The 2D Fourier transform enables us to filter
the positive panel involves the amplitudes of the seismic data in 2D and to suppress some spe-
primary and multiple reflections, direct wave cific correlated noise types. Basically, the pro-
and refractions, while the negative panel com- cess is as follows (Fig. 5.66): the f-k spectrum is
prises spatially aliased signals, back-scattered calculated by computing the 2D Fourier trans-
amplitudes and the events with negative dip, form of the input seismic data. Amplitudes of
such as tail buoy noise. Bird noise and mechan- the events with different dips (or different prop-
ical cable noise amplitudes are located in both agation velocities) accumulate in different areas
panels. In general, it is not possible to recognize on the f-k panel according to their wavenumbers
the amplitudes of multiple reflections as an iso- and frequencies. In order to remove a particular
lated amplitude package in the f-k spectra. In event in the time domain data, for instance the
land seismic shot gathers, however, direct and ground-roll in land seismic data, the area in
refracted wave amplitudes, as well as air waves, the f-k domain that contains the amplitudes of
appear in both panels of the f-k spectrum. In that particular event is multiplied by a small
addition, surface waves, known as ground-roll, coefficient close to zero. The reason that the
are quite dominant on the f-k spectra, and their amplitudes are not multiplied by zero is based
respective amplitudes are prominent packages on the Fourier theory: If we multiply the ampli-
isolated from the primary reflections close to tude spectrum by a constant in the frequency
the wavenumber axis of both panels in the f-k domain, this means that the function is scaled
FIG. 5.65 Negative and positive panels of an f-k spectrum and f-k domain appearance of common events encountered in
marine shot gathers.