Page 273 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 273
258 CARBON NANOTUBES, PILLARED CLAYS, AND POLYMERIC RESINS
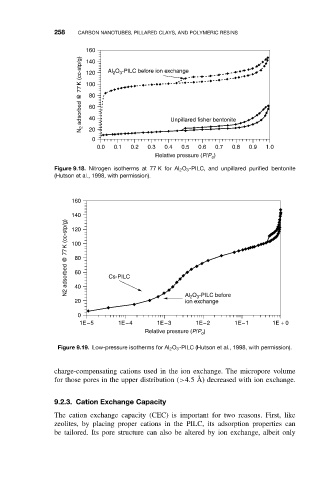
160 Al 2 O 3 -PILC before ion exchange
N 2 adsorbed @ 77 K (cc-stp/g) 120
140
100
80
60
40
20
0 Unpillared fisher bentonite
0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
Relative pressure (P/P o )
Figure 9.18. Nitrogen isotherms at 77 K for Al 2 O 3 -PILC, and unpillared purified bentonite
(Hutson et al., 1998, with permission).
160
140
N2 adsorbed @ 77 K (cc-stp/g) 100 Cs-PILC
120
80
60
40
20 Al 2 O 3 -PILC before
ion exchange
0
1E−5 1E−4 1E−3 1E−2 1E−1 1E + 0
Relative pressure (P/P o )
Figure 9.19. Low-pressure isotherms for Al 2 O 3 -PILC (Hutson et al., 1998, with permission).
charge-compensating cations used in the ion exchange. The micropore volume
for those pores in the upper distribution (>4.5 ˚ A) decreased with ion exchange.
9.2.3. Cation Exchange Capacity
The cation exchange capacity (CEC) is important for two reasons. First, like
zeolites, by placing proper cations in the PILC, its adsorption properties can
be tailored. Its pore structure can also be altered by ion exchange, albeit only