Page 314 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 314
AIR SEPARATION 299
oxygen-binding ability. The rationale for this approach is given first and some
of the results follow.
A basic understanding of the atomic orbitals will help in the understanding
of the stability problem. Comparing the ionic salts of Co, Co 2+ is more stable
7
0
than Co 3+ since the outer-shell orbitals for Co 2+ are 3d ,4s whereas that of
0
6
Co 3+ are 3d ,4s . However, the orbital occupations differ when ligands are
attached to the carbon to form a coordination complex. In order for Co 2+ to
coordinate six ligands, six electrons are in three of the 3d orbitals, to evacuate
2
two 3d orbitals to hybridize with one 4s and three 4p orbitals to form six d sp 3
hybridized orbitals. These six hybridized orbitals form coordination bonds with
six ligands. The seventh electron in the 3d orbitals in Co 2+ is excited to the 5s
orbital, the next higher available orbital. Consequently, this electron can be easily
lost, which is the reason that Co 3+ is more stable than Co 2+ in the coordination
complex.
With this understanding, Hutson and Yang (2000b) first ion-exchanged Co 2+
on anion sites of a substrate (i.e., a cation exchanger) to form stable Co ,and
2+
subsequently attached ligands (usually four) to Co 2+ in order to give Co 2+ the O 2
binding ability. Three different substrates were used: LSX zeolites, mesoporous
MCM-41, and ion-exchange resin.
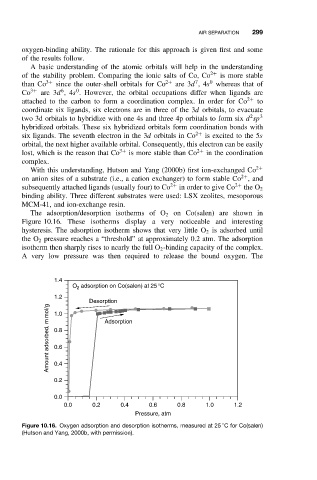
The adsorption/desorption isotherms of O 2 on Co(salen) are shown in
Figure 10.16. These isotherms display a very noticeable and interesting
hysteresis. The adsorption isotherm shows that very little O 2 is adsorbed until
the O 2 pressure reaches a “threshold” at approximately 0.2 atm. The adsorption
isotherm then sharply rises to nearly the full O 2 -binding capacity of the complex.
A very low pressure was then required to release the bound oxygen. The
1.4
O adsorption on Co(salen) at 25°C
2
1.2
Desorption
Amount adsorbed, m mol/g 0.8 Adsorption
1.0
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2
Pressure, atm
◦
Figure 10.16. Oxygen adsorption and desorption isotherms, measured at 25 C for Co(salen)
(Hutson and Yang, 2000b, with permission).