Page 371 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 371
356 SORBENTS FOR APPLICATIONS
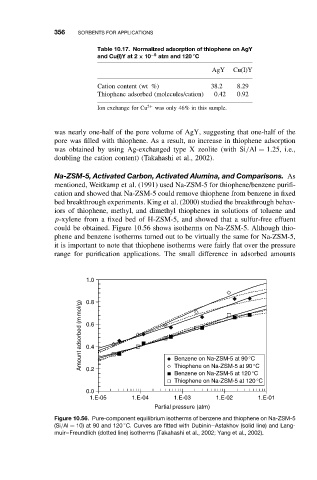
Table 10.17. Normalized adsorption of thiophene on AgY
◦
and Cu(I)Y at 2 × 10 −5 atm and 120 C
AgY Cu(I)Y
Cation content (wt %) 38.2 8.29
Thiophene adsorbed (molecules/cation) 0.42 0.92
Ion exchange for Cu 2+ was only 46% in this sample.
was nearly one-half of the pore volume of AgY, suggesting that one-half of the
pore was filled with thiophene. As a result, no increase in thiophene adsorption
was obtained by using Ag-exchanged type X zeolite (with Si/Al = 1.25, i.e.,
doubling the cation content) (Takahashi et al., 2002).
Na-ZSM-5, Activated Carbon, Activated Alumina, and Comparisons. As
mentioned, Weitkamp et al. (1991) used Na-ZSM-5 for thiophene/benzene purifi-
cation and showed that Na-ZSM-5 could remove thiophene from benzene in fixed
bed breakthrough experiments. King et al. (2000) studied the breakthrough behav-
iors of thiophene, methyl, and dimethyl thiophenes in solutions of toluene and
p-xylene from a fixed bed of H-ZSM-5, and showed that a sulfur-free effuent
could be obtained. Figure 10.56 shows isotherms on Na-ZSM-5. Although thio-
phene and benzene isotherms turned out to be virtually the same for Na-ZSM-5,
it is important to note that thiophene isotherms were fairly flat over the pressure
range for purification applications. The small difference in adsorbed amounts
1.0
0.8
Amount adsorbed (m mol/g) 0.6
0.4
Benzene on Na-ZSM-5 at 90°C
Thiophene on Na-ZSM-5 at 90°C
0.2
Benzene on Na-ZSM-5 at 120°C
Thiophene on Na-ZSM-5 at 120°C
0.0
1.E-05 1.E-04 1.E-03 1.E-02 1.E-01
Partial pressure (atm)
Figure 10.56. Pure-component equilibrium isotherms of benzene and thiophene on Na-ZSM-5
◦
(Si/Al = 10) at 90 and 120 C. Curves are fitted with Dubinin–Astakhov (solid line) and Lang-
muir–Freundlich (dotted line) isotherms (Takahashi et al., 2002; Yang et al., 2002).