Page 335 - Adsorption, Ion Exchange & Catalysis- 2007, Elsevier - Copy
P. 335
Else_AIEC-INGLE_cH004.qxd 7/1/2006 6:54 PM Page 331
4.2 Design of Adsorption and Ion-Exchange Processes 331
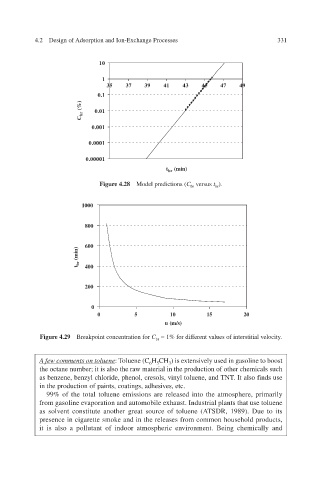
10
1
35 37 39 41 43 45 47 49
0.1
0.01
(%)
br
C
0.001
0.0001
0.00001
(min)
t br
Figure 4.28 Model predictions ( C br versus t ).
br
1000
800
600
(min)
br 400
t
200
0
0 5 10 15 20
u (m/s)
Figure 4.29 Breakpoint concentration for C br . ferent v = 1% for difalues of interstitial v elocity
A f e w comments on toluene : T oluene (C H CH ) is extensively used in gasoline to boost
6 5 3
the octane number; it is also the raw material in the production of other chemicals such
as benzene, benzyl chloride, phenol, cresols, vinyl toluene, and TNT. It also finds use
in the production of paints, coatings, adhesi etc. es, v
99% of the total toluene emissions are released into the atmosphere, primarily
v
from gasoline eaporation and automobile exhaust. Industrial plants that use toluene
TSDR,
as solvent constitute another great source of toluene (A 1989). Due to its
presence in cigarette smoke and in the releases from common household products,
it is also a pollutant of indoor atmospheric environment. Being chemically and