Page 1086 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 1086
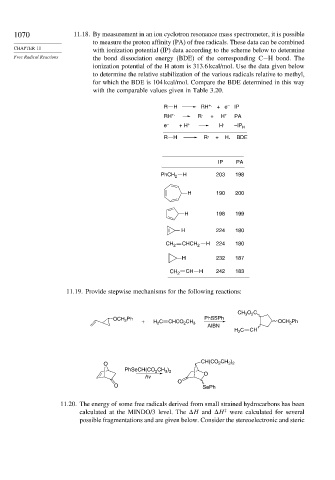
1070 11.18. By measurement in an ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer, it is possible
to measure the proton affinity (PA) of free radicals. These data can be combined
CHAPTER 11 with ionization potential (IP) data according to the scheme below to determine
Free Radical Reactions the bond dissociation energy (BDE) of the corresponding C−H bond. The
ionization potential of the H atom is 313.6 kcal/mol. Use the data given below
to determine the relative stabilization of the various radicals relative to methyl,
for which the BDE is 104 kcal/mol. Compare the BDE determined in this way
with the comparable values given in Table 3.20.
R H RH +. + e – IP
RH +. R . + H + PA
e – + H + H . –IP H
R H R . + H. BDE
IP PA
PhCH 2 H 203 198
H 190 200
H 198 199
H 224 180
CH 2 CHCH 2 H 224 180
H 232 187
CH 2 CH H 242 183
11.19. Provide stepwise mechanisms for the following reactions:
CH 3 O 2 C
OCH 2 Ph PhSSPh
+ H 2 C CHCO 2 CH 3 OCH 2 Ph
AIBN
H 2 C CH
CH(CO CH )
O 2 3 2
PhSeCH(CO CH )
2
3 2
hv O
O
O SePh
11.20. The energy of some free radicals derived from small strained hydrocarbons has been
‡
calculated at the MINDO/3 level. The H and H were calculated for several
possible fragmentations and are given below. Consider the stereoelectronic and steric