Page 1136 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 1136
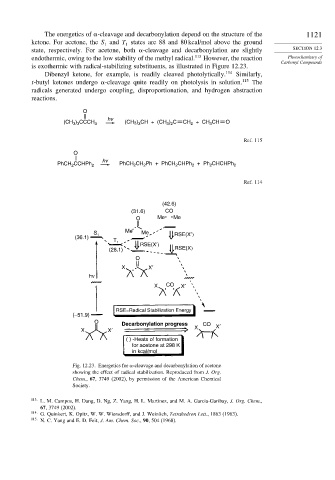
The energetics of -cleavage and decarbonylation depend on the structure of the 1121
ketone. For acetone, the S and T states are 88 and 80 kcal/mol above the ground
1 1
state, respectively. For acetone, both -cleavage and decarbonylation are slightly SECTION 12.3
endothermic, owing to the low stability of the methyl radical. 113 However, the reaction Photochemistry of
Carbonyl Compounds
is exothermic with radical-stabilizing substituents, as illustrated in Figure 12.23.
Dibenzyl ketone, for example, is readily cleaved photolytically. 114 Similarly,
t-butyl ketones undergo -cleavage quite readily on photolysis in solution. 115 The
radicals generated undergo coupling, disproportionation, and hydrogen abstraction
reactions.
O
hv
(CH ) CCCH 3 (CH 3) CH + (CH ) C CH + CH CH O
3 2
2
3
3 3
3
Ref. 115
O
hv
PhCH CCHPh 2 PhCH 2 CH Ph + PhCH CHPh + Ph CHCHPh 2
2
2
2
2
2
Ref. 114
(42.6)
(31.6) CO
O Me Me
S 1 Me Me RSE(X′)
(36.1)
T 1 RSE(X′)
(28.1) RSE(X)
O
X X′
hv
X CO X′
RSE=Radical Stabilization Energy
(–51.9)
O
Decarbonylation progress CO X′
X X′ X
( ) -Heats of formation
for acetone at 298 K
in kcal/mol
Fig. 12.23. Energetics for -cleavage and decarbonylation of acetone
showing the effect of radical stabilization. Reproduced from J. Org.
Chem., 67, 3749 (2002), by permission of the American Chemical
Society.
113 L. M. Campos, H. Dang, D. Ng, Z. Yang, H. L. Martinez, and M. A. Garcia-Garibay, J. Org. Chem.,
67, 3749 (2002).
114 G. Quinkert, K. Opitz, W. W. Wiersdorff, and J. Weinlich, Tetrahedron Lett., 1863 (1963).
115
N. C. Yang and E. D. Feit, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 90, 504 (1968).