Page 244 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 244
224 Enantioselective acylation of amines is generally more challenging and less explored,
although good results have been reported in some cases. A number of 1-
CHAPTER 2 phenylethylamines and 4-phenylbutane-2-amine were resolved using an acylase from
Stereochemistry, Alcaligenes faecalis.
Conformation,
and Stereoselectivity
NH 2 NHCOCH Ph
2
CH 3 + PhCH CONH 2 A. faecalis CH 3
2
penicillin
acylase
99.3% e.e. at
49% conversion
Ref. 233
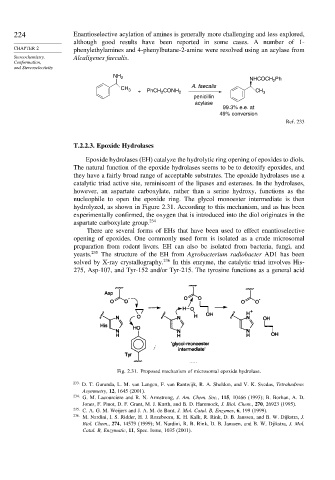
T.2.2.3. Epoxide Hydrolases
Epoxide hydrolases (EH) catalyze the hydrolytic ring opening of epoxides to diols.
The natural function of the epoxide hydrolases seems to be to detoxify epoxides, and
they have a fairly broad range of acceptable substrates. The epoxide hydrolases use a
catalytic triad active site, reminiscent of the lipases and esterases. In the hydrolases,
however, an aspartate carboxylate, rather than a serine hydroxy, functions as the
nucleophile to open the epoxide ring. The glycol monoester intermediate is then
hydrolyzed, as shown in Figure 2.31. According to this mechanism, and as has been
experimentally confirmed, the oxygen that is introduced into the diol originates in the
aspartate carboxylate group. 234
There are several forms of EHs that have been used to effect enantioselective
opening of epoxides. One commonly used form is isolated as a crude microsomal
preparation from rodent livers. EH can also be isolated from bacteria, fungi, and
yeasts. 235 The structure of the EH from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1 has been
solved by X-ray crystallography. 236 In this enzyme, the catalytic triad involves His-
275, Asp-107, and Tyr-152 and/or Tyr-215. The tyrosine functions as a general acid
Fig. 2.31. Proposed mechanism of microsomal epoxide hydrolase.
233
D. T. Guranda, L. M. van Langen, F. van Rantwijk, R. A. Sheldon, and V. K. Svedas, Tetrahedron:
Asymmetry, 12, 1645 (2001).
234 G. M. Lacourciere and R. N. Armstrong, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 115, 10466 (1993); B. Borhan, A. D.
Jones, F. Pinot, D. F. Grant, M. J. Kurth, and B. D. Hammock, J. Biol. Chem., 270, 26923 (1995).
235
C. A. G. M. Weijers and J. A. M. de Bont, J. Mol. Catal. B, Enzymes, 6, 199 (1999).
236
M. Nardini, I. S. Ridder, H. J. Rozeboom, K. H. Kalk, R. Rink, D. B. Janssen, and B. W. Dijkstra, J.
Biol. Chem., 274, 14579 (1999); M. Nardini, R. B. Rink, D. B. Janssen, and B. W. Djikstra, J. Mol.
Catal. B, Enzymatic, 11, Spec. Issue, 1035 (2001).