Page 246 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 246
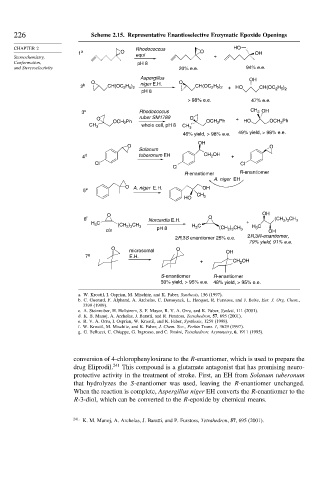
226 Scheme 2.15. Representative Enantioselective Enzymatic Epoxide Openings
CHAPTER 2 Rhodococcus HO
1 a O O OH
Stereochemistry, equi +
Conformation, pH 8
and Stereoselectivity 20% e.e. 94% e.e.
Aspergillus OH
O niger E.H. O
2 b CH(OC 2 H 5 ) 2 CH(OC 2 H 5 ) 2 + HO CH(OC 2 H 5 ) 2
pH 8
> 98% e.e. 47% e.e.
3 c Rhodococcus CH 3 OH
O ruber SM1789 O +
OCH 2 Ph OCH 2 Ph HO OCH 2 Ph
CH 3 whole cell, pH 8 CH 3
46% yield, > 98% e.e. 49% yield, > 98% e.e.
OH
O O
Solanum
4 d tuberonum EH CH 2 OH +
Cl Cl
Cl
R-enantiomer R-enantiomer
A. niger EH
5 e O A. niger E.H. OH
HO CH 3
O OH
6 f Norcardia E.H. O (CH 2 ) 3 CH 3
H 3 C +
(CH 2 ) 3 CH 3 H 3 C H 3 C
cis pH 8 (CH 2 ) 3 CH 3 OH
2R,3R-enantiomer,
2R,3S enantiomer 25% e.e.
79% yield, 91% e.e.
O O
microsomal OH
7 g E.H.
+ CH 2 OH
S-enantiomer R-enantiomer
50% yield, > 95% e.e. 48% yield, > 95% e.e.
a. W. Kroutil, I. Osprian, M. Mischitz, and K. Faber, Synthesis, 156 (1997).
b. C. Guerard, F. Alphand, A. Archelas, C. Demuynck, L. Hecquet, R. Furstoss, and J. Bolte, Eur. J. Org. Chem.,
3399 (1999).
c. A. Steinreiber, H. Hellstrom, S. F. Mayer, R. V. A. Orru, and K. Faber, Synlett, 111 (2001).
d. K. B. Manoj, A. Archelas, J. Baratti, and R. Furstoss, Tetrahedron, 57, 695 (2001).
e. R. V. A. Orru, I. Osprian, W. Kroutil, and K. Faber, Synthesis, 1259 (1998).
f. W. Kroutil, M. Mischitz, and K. Faber, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 3629 (1997).
g. G. Bellucci, C. Chiappe, G. Ingrosso, and C. Rosini, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 6, 1911 (1995).
conversion of 4-chlorophenyloxirane to the R-enantiomer, which is used to prepare the
drug Eliprodil. 241 This compound is a glutamate antagonist that has promising neuro-
protective activity in the treatment of stroke. First, an EH from Solanum tuberonum
that hydrolyzes the S-enantiomer was used, leaving the R-enantiomer unchanged.
When the reaction is complete, Aspergillus niger EH converts the R-enantiomer to the
R-3-diol, which can be converted to the R-epoxide by chemical means.
241
K. M. Manoj, A. Archelas, J. Baratti, and P. Furstoss, Tetrahedron, 57, 695 (2001).