Page 525 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 525
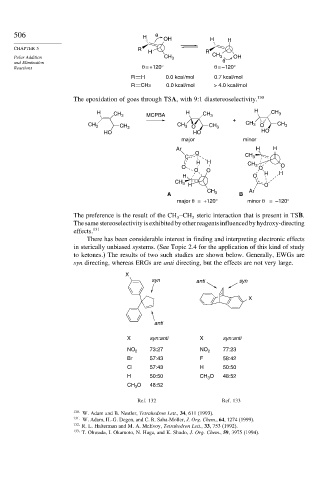
506 H θ OH H H
CHAPTER 5 R H R
Polar Addition CH 3 CH 3 OH
and Elimination θ
Reactions θ = +120° θ = –120°
R H 0.0 kcal/mol 0.7 kcal/mol
R CH3 0.0 kcal/mol > 4.0 kcal/mol
The epoxidation of goes through TSA, with 9:1 diastereoselectivity. 130
H CH 3 MCPBA H CH 3 H CH 3
+
CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 O CH 3 CH 3 O CH 3
HO HO HO
major minor
Ar H H
O
C CH 3
H H
O CH 3 O O
O O H
H O H
CH 3
H O
Ar
CH 3
A B
major θ = +120° minor θ = –120°
The preference is the result of the CH –CH steric interaction that is present in TSB.
3
3
Thesamestereoselectivityisexhibitedbyotherreagentsinfluencedbyhydroxy-directing
effects. 131
There has been considerable interest in finding and interpreting electronic effects
in sterically unbiased systems. (See Topic 2.4 for the application of this kind of study
to ketones.) The results of two such studies are shown below. Generally, EWGs are
syn directing, whereas ERGs are anti directing, but the effects are not very large.
X
syn anti syn
X
anti
X syn:anti X syn:anti
NO 2 73:27 NO 2 77:23
Br 57:43 F 58:42
Cl 57:43 H 50:50
H 50:50 CH O 48:52
3
CH O 48:52
3
Ref. 132 Ref. 133
130
W. Adam and B. Nestler, Tetrahedron Lett., 34, 611 (1993).
131 W. Adam, H.-G. Degen, and C. R. Saha-Moller, J. Org. Chem., 64, 1274 (1999).
132 R. L. Halterman and M. A. McEvoy, Tetrahedron Lett., 33, 753 (1992).
133
T. Ohwada, I. Okamoto, N. Haga, and K. Shudo, J. Org. Chem., 59, 3975 (1994).