Page 726 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 726
708 0
CHAPTER 7 –1
Addition, Condensation
log k obsd (s –1 )
and Substitution –2
Reactions of Carbonyl
Compounds –3
–4
–5
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
pH
–2.0
log k obsd (s –1 )
–3.0
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
pH
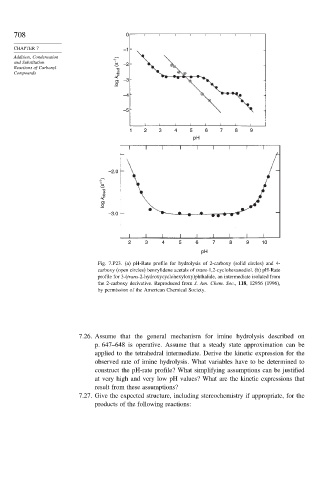
Fig. 7.P23. (a) pH-Rate profile for hydrolysis of 2-carboxy (solid circles) and 4-
carboxy (open circles) benzylidene acetals of trans-1,2-cyclohexanediol. (b) pH-Rate
profile for 3-(trans-2-hydroxycyclohexyloxy)phthalide, an intermediate isolated from
the 2-carboxy derivative. Reproduced from J. Am. Chem. Soc., 118, 12956 (1996),
by permission of the American Chemical Society.
7.26. Assume that the general mechanism for imine hydrolysis described on
p. 647–648 is operative. Assume that a steady state approximation can be
applied to the tetrahedral intermediate. Derive the kinetic expression for the
observed rate of imine hydrolysis. What variables have to be determined to
construct the pH-rate profile? What simplifying assumptions can be justified
at very high and very low pH values? What are the kinetic expressions that
result from these assumptions?
7.27. Give the expected structure, including stereochemistry if appropriate, for the
products of the following reactions: