Page 722 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 722
704
Series I, substituent in Ar Series II, substituent in Ar
CHAPTER 7
X a
X a
Addition, Condensation k cat k cat
and Substitution 2 7×10 −4 1.05 8 85×10 −2 0.49
Reactions of Carbonyl m-NO 2 −3 m-NO 2 −2
Compounds m-F 2 2×10 0.92 m-Br 4 7×10 0.65
m-CH 3 O 9 6×10 −3 0.78 m-F 2 45×10 −2 0.67
H 1 3×10 −2 0.77 m-CH 3 O 2 55×10 −2 0.71
1 1×10 −1 0.72 H 1 3×10 −2 0.77
p-CH 3
p-CH 3 O 2 8×10 −1 0.68 p-CH 3 1 3×10 −2 0.88
p-CH 3 O 1 65×10 −2 0.96
a. Rate constant in s −1 for catalysis by acetic acid.
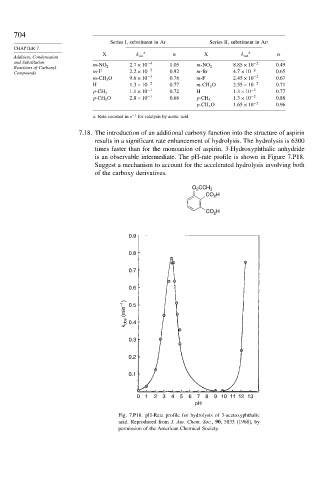
7.18. The introduction of an additional carboxy function into the structure of aspirin
results in a significant rate enhancement of hydrolysis. The hydrolysis is 6300
times faster than for the monoanion of aspirin. 3-Hydroxyphthalic anhydride
is an observable intermediate. The pH-rate profile is shown in Figure 7.P18.
Suggest a mechanism to account for the accelerated hydrolysis involving both
of the carboxy derivatives.
O CCH 3
2
CO H
2
CO H
2
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
k obs (min –1 ) 0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
01 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
pH
Fig. 7.P18. pH-Rate profile for hydrolysis of 3-acetoxyphthalic
acid. Reproduced from J. Am. Chem. Soc., 90, 5833 (1968), by
permission of the American Chemical Society.