Page 721 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 721
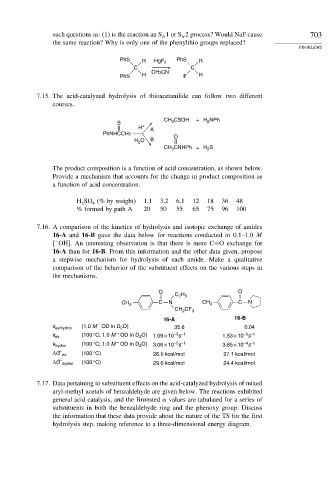
such questions as: (1) is the reaction an S 1orS 2 process? Would NaF cause 703
N
N
the same reaction? Why is only one of the phenylthio groups replaced?
PROBLEMS
PhS R HgF 2 PhS R
C C
CH3CN
PhS H F H
7.15. The acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of thioacetanilide can follow two different
courses.
CH CSOH + H NPh
S 3 2
H + A
PhNHCCH3 O
H O B
2
CH CNHPh + H S
3
2
The product composition is a function of acid concentration, as shown below.
Provide a mechanism that accounts for the change in product composition as
a function of acid concentration.
H SO (% by weight) 1.1 3.2 6.1 12 18 36 48
4
2
% formed by path A 20 50 55 65 75 96 100
7.16. A comparison of the kinetics of hydrolysis and isotopic exchange of amides
16-A and 16-B gave the data below for reactions conducted in 0.1–1.0 M
−
[ OH]. An interesting observation is that there is more C=O exchange for
16-A than for 16-B. From this information and the other data given, propose
a stepwise mechanism for hydrolysis of each amide. Make a qualitative
comparison of the behavior of the substituent effects on the various steps in
the mechanisms.
O O
C H
2 5
CH 3 C N CH 3 C N
CH CF 3
2
16-A 16-B
–
k ex/hydrol (1.0 M OD in D O) 35.6 0.04
2
–
–5 –1
–3 –1
k ex (100 °C; 1.0 M OD in D O) 1.09 × 10 s 1.53 × 10 s
2
–
–5 –1
–4 –1
k hydrol (100 °C; 1.0 M OD in D O) 3.06 × 10 s 3.85 × 10 s
2
∗
ΔG ex (100 °C) 26.5 kcal/mol 27.1 kcal/mol
∗
ΔG hydrol (100 °C) 29.6 kcal/mol 24.4 kcal/mol
7.17. Data pertaining to substituent effects on the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of mixed
aryl-methyl acetals of benzaldehyde are given below. The reactions exhibited
general acid catalysis, and the Brønsted
values are tabulated for a series of
substituents in both the benzaldehyde ring and the phenoxy group. Discuss
the information that these data provide about the nature of the TS for the first
hydrolysis step, making reference to a three-dimensional energy diagram.