Page 1129 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 1129
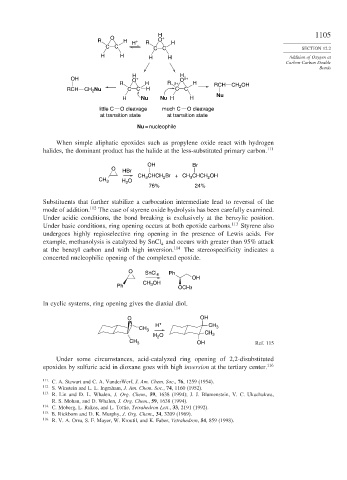
H 1105
O +
R H H + R O H
C C C C SECTION 12.2
H H H H Addition of Oxygen at
Carbon-Carbon Double
Bonds
H H
OH O + O δ+
R H R δ+ H RCH CH OH
RCH CH Nu C C H C C 2
2
Nu
H Nu Nu H H
little C O cleavage much C O cleavage
at transition state at transition state
Nu = nucleophile
When simple aliphatic epoxides such as propylene oxide react with hydrogen
halides, the dominant product has the halide at the less-substituted primary carbon. 111
OH Br
O HBr
CHCH Br + CH CHCH OH
CH 3 2 3 2
CH 3 H O
2
76% 24%
Substituents that further stabilize a carbocation intermediate lead to reversal of the
mode of addition. 112 The case of styrene oxide hydrolysis has been carefully examined.
Under acidic conditions, the bond breaking is exclusively at the benzylic position.
Under basic conditions, ring opening occurs at both epoxide carbons. 113 Styrene also
undergoes highly regioselective ring opening in the presence of Lewis acids. For
example, methanolysis is catalyzed by SnCl and occurs with greater than 95% attack
4
at the benzyl carbon and with high inversion. 114 The stereospecificity indicates a
concerted nucleophilic opening of the complexed epoxide.
O SnCl Ph
4
OH
CH OH
Ph 3
OCH3
In cyclic systems, ring opening gives the diaxial diol.
O OH
H + CH 3
CH 3
CH
H O 3
2
CH 3 OH Ref. 115
Under some circumstances, acid-catalyzed ring opening of 2,2-disubstituted
epoxides by sulfuric acid in dioxane goes with high inversion at the tertiary center. 116
111
C. A. Stewart and C. A. VanderWerf, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 76, 1259 (1954).
112 S. Winstein and L. L. Ingraham, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 74, 1160 (1952).
113
R. Lin and D. L. Whalen, J. Org. Chem., 59, 1638 (1994); J. J. Blumenstein, V. C. Ukachukwa,
R. S. Mohan, and D. Whalen, J. Org. Chem., 59, 1638 (1994).
114 C. Moberg, L. Rakos, and L. Tottie, Tetrahedron Lett., 33, 2191 (1992).
115 B. Rickborn and D. K. Murphy, J. Org. Chem., 34, 3209 (1969).
116
R. V. A. Orru, S. F. Mayer, W. Kroutil, and K. Faber, Tetrahedron, 54, 859 (1998).