Page 543 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 543
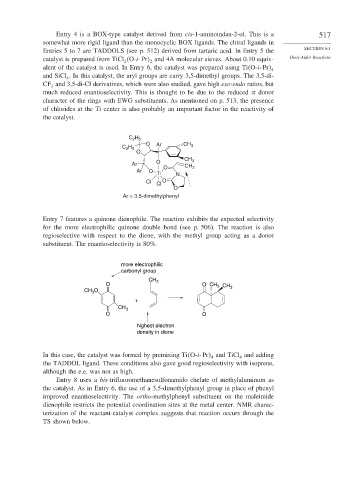
Entry 4 is a BOX-type catalyst derived from cis-1-aminoindan-2-ol. This is a 517
somewhat more rigid ligand than the monocyclic BOX ligands. The chiral ligands in
Entries 5 to 7 are TADDOLS (see p. 512) derived from tartaric acid. In Entry 5 the SECTION 6.1
catalyst is prepared from TiCl O-i-Pr and 4A molecular sieves. About 0.10 equiv- Diels-Alder Reactions
2
2
alent of the catalyst is used. In Entry 6, the catalyst was prepared using Ti O-i-Pr 4
and SiCl . In this catalyst, the aryl groups are carry 3,5-dimethyl groups. The 3,5-di-
4
CF and 3,5-di-Cl derivatives, which were also studied, gave high exo:endo ratios, but
3
much reduced enantioselectivity. This is thought to be due to the reduced donor
character of the rings with EWG substituents. As mentioned on p. 513, the presence
of chlorides at the Ti center is also probably an important factor in the reactivity of
the catalyst.
H
C 2 5
O Ar CH
C H 3
2 5
O
Ar O CH 3
O CH 2
Ar O Ti N
Cl Cl O
O
Ar = 3,5-dimethylphenyl
Entry 7 features a quinone dienophile. The reaction exhibits the expected selectivity
for the more electrophilic quinone double bond (see p. 506). The reaction is also
regioselective with respect to the diene, with the methyl group acting as a donor
substituent. The enantioselectivity is 80%.
more electrophilic
carbonyl group
CH 3
O O CH 3 CH
CH O 3
3
+
CH 3
O O
highest electron
density in diene
In this case, the catalyst was formed by premixing Ti O-i-Pr and TiCl and adding
4 4
the TADDOL ligand. These conditions also gave good regioselectivity with isoprene,
although the e.e. was not as high.
Entry 8 uses a bis-trifluoromethanesulfonamido chelate of methylaluminum as
the catalyst. As in Entry 6, the use of a 3,5-dimethylphenyl group in place of phenyl
improved enantioselectivity. The ortho-methylphenyl substituent on the maleimide
dienophile restricts the potential coordination sites at the metal center. NMR charac-
terization of the reactant-catalyst complex suggests that reaction occurs through the
TS shown below.