Page 623 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 623
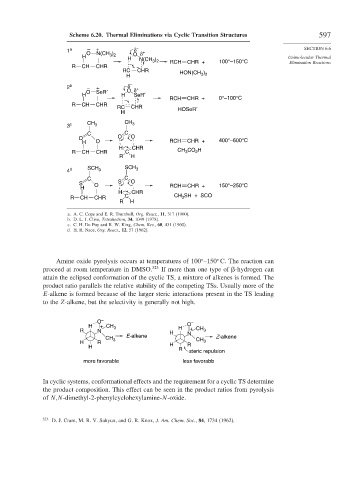
Scheme 6.20. Thermal Eliminations via Cyclic Transition Structures 597
δ
–
–
1 a O + N(CH ) O δ + SECTION 6.6
H 3 2 Unimolecular Thermal
H N(CH ) RCH CHR + 100°–150°C Elimination Reactions
3 2
R CH CHR
RC CHR
)
HON(CH 3 2
H
δ
–
2 b – + O δ +
O SeR′
H H SeR′
RCH CHR + 0°–100°C
R CH CHR
RC CHR HOSeR′
H
CH
3 c CH 3 3
C C
O O O 400°–600°C
H O RCH CHR +
H CHR
R CH CHR C CH CO H
3
2
R H
4 d SCH 3 SCH 3
C C
S O S O RCH CHR + 150°–250°C
H
H CHR
R CH CHR C CH SH + SCO
3
R H
a. A. C. Cope and E. R. Trumbull, Org. React., 11, 317 (1960).
b. D. L. J. Clive, Tetrahedron, 34, 1049 (1978).
c. C. H. De Puy and R. W. King, Chem. Rev., 60, 431 (1960).
d. H. R. Nace, Org. React., 12, 57 (1962).
Amine oxide pyrolysis occurs at temperatures of 100 –150 C. The reaction can
proceed at room temperature in DMSO. 323 If more than one type of -hydrogen can
attain the eclipsed conformation of the cyclic TS, a mixture of alkenes is formed. The
product ratio parallels the relative stability of the competing TSs. Usually more of the
E-alkene is formed because of the larger steric interactions present in the TS leading
to the Z-alkene, but the selectivity is generally not high.
O – –
H + CH 3 O
R N H H + CH 3
E-alkene N Z-alkene
CH 3
H R H CH 3
H R
R
steric repulsion
more favorable less favorable
In cyclic systems, conformational effects and the requirement for a cyclic TS determine
the product composition. This effect can be seen in the product ratios from pyrolysis
of N,N-dimethyl-2-phenylcyclohexylamine-N-oxide.
323
D. J. Cram, M. R. V. Sahyun, and G. R. Knox, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 84, 1734 (1962).