Page 69 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 69
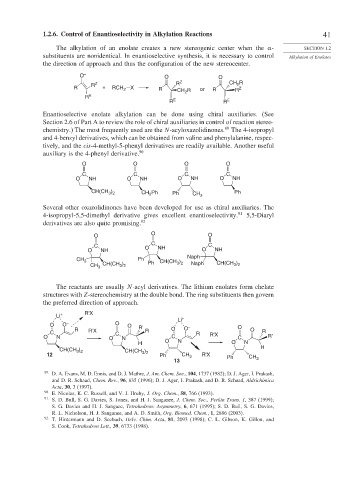
1.2.6. Control of Enantioselectivity in Alkylation Reactions 41
The alkylation of an enolate creates a new stereogenic center when the - SECTION 1.2
substituents are nonidentical. In enantioselective synthesis, it is necessary to control Alkylation of Enolates
the direction of approach and thus the configuration of the new stereocenter.
O – O O
2
R Z R Z CH R
R + RCH 2 X R CH R or R R Z
2
R E
R E R E
Enantioselective enolate alkylation can be done using chiral auxiliaries. (See
Section 2.6 of Part A to review the role of chiral auxiliaries in control of reaction stereo-
89
chemistry.) The most frequently used are the N-acyloxazolidinones. The 4-isopropyl
and 4-benzyl derivatives, which can be obtained from valine and phenylalanine, respec-
tively, and the cis-4-methyl-5-phenyl derivatives are readily available. Another useful
auxiliary is the 4-phenyl derivative. 90
O O O O
C C C C
O NH O NH O NH O NH
CH(CH ) CH 2 Ph Ph CH 3 Ph
3 2
Several other oxazolidinones have been developed for use as chiral auxiliaries. The
4-isopropyl-5,5-dimethyl derivative gives excellent enantioselectivity. 91 5,5-Diaryl
derivatives are also quite promising. 92
O O O
C
C O NH C
O NH O NH
CH 3 Ph ) Naph
)
CH 3 CH(CH ) Ph CH(CH 3 2 Naph CH(CH 3 2
3 2
The reactants are usually N-acyl derivatives. The lithium enolates form chelate
structures with Z-stereochemistry at the double bond. The ring substituents then govern
the preferred direction of approach.
Li + R'X
Li +
O O – O O – O
R R' O O O
C R'X C R R R
O N O N C R'X C R'
H O N O N
CH(CH ) ) H
3 2
12 CH(CH 3 2 Ph CH 3 R'X Ph CH
13 3
89
D. A. Evans, M. D. Ennis, and D. J. Mathre, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 104, 1737 (1982); D. J. Ager, I. Prakash,
and D. R. Schaad, Chem. Rev., 96, 835 (1996); D. J. Ager, I. Prakash, and D. R. Schaad, Aldrichimica
Acta, 30, 3 (1997).
90 E. Nicolas, K. C. Russell, and V. J. Hruby, J. Org. Chem., 58, 766 (1993).
91
S. D. Bull, S. G. Davies, S. Jones, and H. J. Sanganee, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 387 (1999);
S. G. Davies and H. J. Sangaee, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 6, 671 (1995); S. D. Bull, S. G. Davies,
R. L. Nicholson, H. J. Sanganee, and A. D. Smith, Org. Biomed. Chem., 1, 2886 (2003).
92 T. Hintermann and D. Seebach, Helv. Chim. Acta, 81, 2093 (1998); C. L. Gibson, K. Gillon, and
S. Cook, Tetrahedron Lett., 39, 6733 (1998).