Page 895 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 895
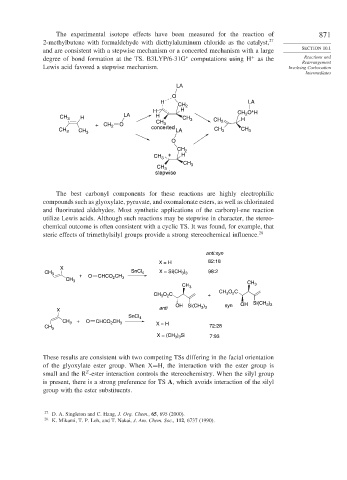
The experimental isotope effects have been measured for the reaction of 871
2-methylbutene with formaldehyde with diethylaluminum chloride as the catalyst, 27
and are consistent with a stepwise mechanism or a concerted mechanism with a large SECTION 10.1
∗
+
degree of bond formation at the TS. B3LYP/6-31G computations using H as the Reactions and
Rearrangement
Lewis acid favored a stepwise mechanism. Involving Carbocation
Intermediates
LA
O
H LA
CH 2
+
H H CH O H
CH 3 H LA H CH 3 2
CH CH 2 H
+ CH 2 O 3
CH 3 CH 3 concerted LA CH 3 CH 3
O
CH 2
CH 3 + H
CH
CH 3 3
stepwise
The best carbonyl components for these reactions are highly electrophilic
compounds such as glyoxylate, pyruvate, and oxomalonate esters, as well as chlorinated
and fluorinated aldehydes. Most synthetic applications of the carbonyl-ene reaction
utilize Lewis acids. Although such reactions may be stepwise in character, the stereo-
chemical outcome is often consistent with a cyclic TS. It was found, for example, that
steric effects of trimethylsilyl groups provide a strong stereochemical influence. 28
anti:syn
X = H 82:18
X
SnCl 4 98:2
CH 3 X = Si(CH 3 ) 3
+ O CHCO 2 CH 3
CH 3
CH 3
CH 3
CH 3 O 2 C
CH 3 O 2 C +
OH Si(CH 3 ) 3 syn OH Si(CH 3 ) 3
X anti
SnCl 4
+
CH 3 O CHCO 2 CH 3
X = H 72:28
CH 3
X = (CH 3 ) 3 Si 7:93
These results are consistent with two competing TSs differing in the facial orientation
of the glyoxylate ester group. When X=H, the interaction with the ester group is
Z
small and the R -ester interaction controls the stereochemistry. When the silyl group
is present, there is a strong preference for TS A, which avoids interaction of the silyl
group with the ester substituents.
27 D. A. Singleton and C. Hang, J. Org. Chem., 65, 895 (2000).
28
K. Mikami, T. P. Loh, and T. Nakai, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 112, 6737 (1990).