Page 899 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 899
O O 875
N N
t-Bu Cu t-Bu CO C H SECTION 10.1
CH + O CHCO C H 2 2 5 Reactions and
2
2 2 5
OH Rearrangement
Involving Carbocation
95% yield, 96% e.e. Intermediates
Ref. 41
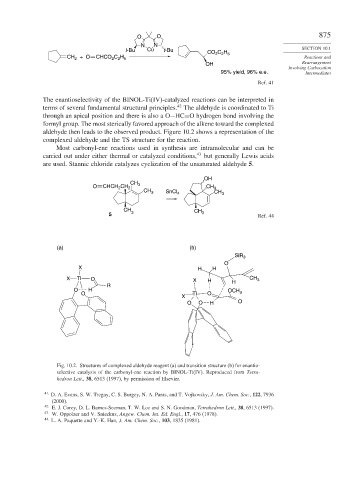
The enantioselectivity of the BINOL-Ti(IV)-catalyzed reactions can be interpreted in
42
terms of several fundamental structural principles. The aldehyde is coordinated to Ti
through an apical position and there is also a O−HC=O hydrogen bond involving the
formyl group. The most sterically favored approach of the alkene toward the complexed
aldehyde then leads to the observed product. Figure 10.2 shows a representation of the
complexed aldehyde and the TS structure for the reaction.
Most carbonyl-ene reactions used in synthesis are intramolecular and can be
carried out under either thermal or catalyzed conditions, 43 but generally Lewis acids
are used. Stannic chloride catalyzes cyclization of the unsaturated aldehyde 5.
OH
CH
O CHCH CH 2 3 CH 3
2
CH 3 SnCl 4 CH 3
CH CH
5 3 3 Ref. 44
(a) (b)
SiR 3
O
X H H
X TI O X H CH 3
R H
O H OCH
O TI O 3
X
O O H O
Fig. 10.2. Structures of complexed aldehyde reagent (a) and transition structure (b) for enantio-
selective catalysis of the carbonyl-ene reaction by BINOL-Ti(IV). Reproduced from Tetra-
hedron Lett., 38, 6513 (1997), by permission of Elsevier.
41 D. A. Evans, S. W. Tregay, C. S. Burgey, N. A. Paras, and T. Vojkovsky, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 122, 7936
(2000).
42
E. J. Corey, D. L. Barnes-Seeman, T. W. Lee and S. N. Goodman, Tetrahedron Lett., 38, 6513 (1997).
43 W. Oppolzer and V. Snieckus, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 17, 476 (1978).
44
L. A. Paquette and Y.-K. Han, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 103, 1835 (1981).