Page 314 - Advances in Renewable Energies and Power Technologies
P. 314
5. Economics of Hybrid PV/Batteries Bank/Diesel Generator System 287
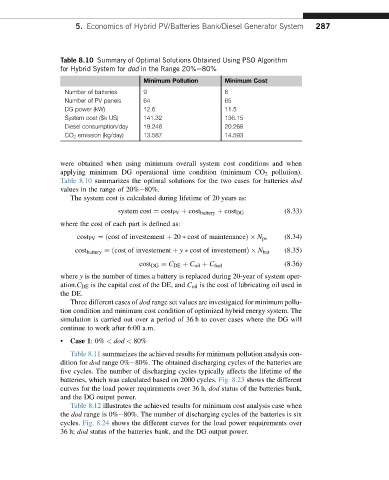
Table 8.10 Summary of Optimal Solutions Obtained Using PSO Algorithm
for Hybrid System for dod in the Range 20%e80%
Minimum Pollution Minimum Cost
Number of batteries 9 6
Number of PV panels 64 65
DG power (kW) 12.6 11.5
System cost ($k US) 141.32 136.15
Diesel consumption/day 19.246 20.268
CO 2 emission (kg/day) 13.587 14.593
were obtained when using minimum overall system cost conditions and when
applying minimum DG operational time condition (minimum CO 2 pollution).
Table 8.10 summarizes the optimal solutions for the two cases for batteries dod
values in the range of 20%e80%.
The system cost is calculated during lifetime of 20 years as:
system cost ¼ cost PV þ cost battery þ cost DG (8.33)
where the cost of each part is defined as:
(8.34)
cost PV ¼ðcost of investement þ 20 cost of maintenanceÞ N pv
cost battery ¼ðcost of investement þ y cost of investementÞ N bat (8.35)
cost DG ¼ C DE þ C oil þ C fuel (8.36)
where y is the number of times a battery is replaced during 20-year of system oper-
ation.C DE is the capital cost of the DE, and C oil is the cost of lubricating oil used in
the DE.
Three different cases of dod range set values are investigated for minimum pollu-
tion condition and minimum cost condition of optimized hybrid energy system. The
simulation is carried out over a period of 36 h to cover cases where the DG will
continue to work after 6:00 a.m.
• Case 1:0% < dod < 80%
Table 8.11 summarizes the achieved results for minimum pollution analysis con-
dition for dod range 0%e80%. The obtained discharging cycles of the batteries are
five cycles. The number of discharging cycles typically affects the lifetime of the
batteries, which was calculated based on 2000 cycles. Fig. 8.23 shows the different
curves for the load power requirements over 36 h, dod status of the batteries bank,
and the DG output power.
Table 8.12 illustrates the achieved results for minimum cost analysis case when
the dod range is 0%e80%. The number of discharging cycles of the batteries is six
cycles. Fig. 8.24 shows the different curves for the load power requirements over
36 h; dod status of the batteries bank, and the DG output power.