Page 332 - Advances in Renewable Energies and Power Technologies
P. 332
3. Photovoltaic Irrigation Systems Components 305
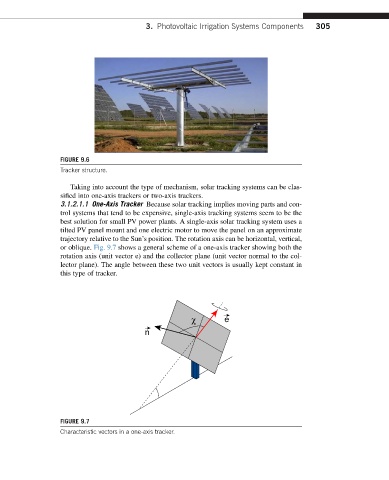
FIGURE 9.6
Tracker structure.
Taking into account the type of mechanism, solar tracking systems can be clas-
sified into one-axis trackers or two-axis trackers.
3.1.2.1.1 One-Axis Tracker Because solar tracking implies moving parts and con-
trol systems that tend to be expensive, single-axis tracking systems seem to be the
best solution for small PV power plants. A single-axis solar tracking system uses a
tilted PV panel mount and one electric motor to move the panel on an approximate
trajectory relative to the Sun’s position. The rotation axis can be horizontal, vertical,
or oblique. Fig. 9.7 shows a general scheme of a one-axis tracker showing both the
rotation axis (unit vector e) and the collector plane (unit vector normal to the col-
lector plane). The angle between these two unit vectors is usually kept constant in
this type of tracker.
χ e
n
FIGURE 9.7
Characteristic vectors in a one-axis tracker.