Page 266 - Air and gas Drilling Field Guide 3rd Edition
P. 266
10.5 Nonfriction and Friction Illustrative Examples 257
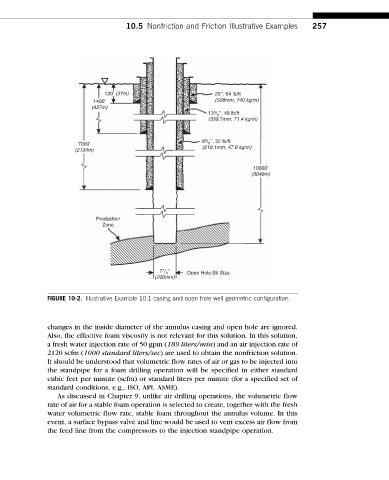
120’ (37m) 20’’, 94 lb/ft
1400’ (508mm, 140 kg/m)
(427m)
3
13 / ’’, 48 lb/ft
8
(339.7mm, 71.4 kg/m)
8 5 / ’’, 32 lb/ft
7000’ 8
(2134m) (219.1mm, 47.6 kg/m)
10000’
(3048m)
Production
Zone
7 7 / ’’ Open Hole Bit Size
8
(200mm)
FIGURE 10-2. Illustrative Example 10.1 casing and open hole well geometric configuration.
changes in the inside diameter of the annulus casing and open hole are ignored.
Also, the effective foam viscosity is not relevant for this solution. In this solution,
a fresh water injection rate of 50 gpm (189 liters/min) and an air injection rate of
2120 scfm (1000 standard liters/sec) are used to obtain the nonfriction solution.
It should be understood that volumetric flow rates of air or gas to be injected into
the standpipe for a foam drilling operation will be specified in either standard
cubic feet per minute (scfm) or standard liters per minute (for a specified set of
standard conditions, e.g., ISO, API, ASME).
As discussed in Chapter 9, unlike air drilling operations, the volumetric flow
rate of air for a stable foam operation is selected to create, together with the fresh
water volumetric flow rate, stable foam throughout the annulus volume. In this
event, a surface bypass valve and line would be used to vent excess air flow from
the feed line from the compressors to the injection standpipe operation.