Page 399 -
P. 399
PROJECT SCHEDULING WITH KNOWN ACTIVITY TIMES 379
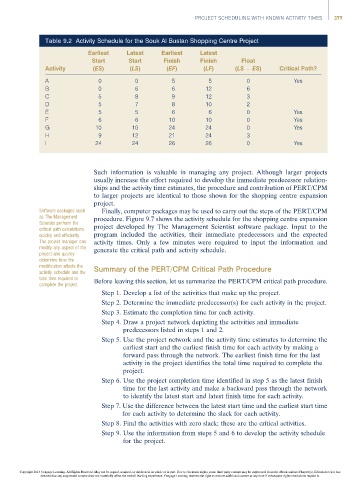
Table 9.2 Activity Schedule for the Souk Al Bustan Shopping Centre Project
Earliest Latest Earliest Latest
Start Start Finish Finish Float
Activity (ES) (LS) (EF) (LF) (LS ES) Critical Path?
A 0 0 5 5 0 Yes
B 0 6 6 12 6
C 5 8 9 12 3
D 5 7 8 10 2
E 5 5 6 6 0 Yes
F 6 6 10 10 0 Yes
G 10 10 24 24 0 Yes
H 9 12 21 24 3
I 24 24 26 26 0 Yes
Such information is valuable in managing any project. Although larger projects
usually increase the effort required to develop the immediate predecessor relation-
ships and the activity time estimates, the procedure and contribution of PERT/CPM
to larger projects are identical to those shown for the shopping centre expansion
project.
Software packages such Finally, computer packages may be used to carry out the steps of the PERT/CPM
as The Management procedure. Figure 9.7 shows the activity schedule for the shopping centre expansion
Scientist perform the
critical path calculations project developed by The Management Scientist software package. Input to the
quickly and efficiently. program included the activities, their immediate predecessors and the expected
The project manager can activity times. Only a few minutes were required to input the information and
modify any aspect of the generate the critical path and activity schedule.
project and quickly
determine how the
modification affects the
activity schedule and the Summary of the PERT/CPM Critical Path Procedure
total time required to
complete the project. Before leaving this section, let us summarize the PERT/CPM critical path procedure.
Step 1. Develop a list of the activities that make up the project.
Step 2. Determine the immediate predecessor(s) for each activity in the project.
Step 3. Estimate the completion time for each activity.
Step 4. Draw a project network depicting the activities and immediate
predecessors listed in steps 1 and 2.
Step 5. Use the project network and the activity time estimates to determine the
earliest start and the earliest finish time for each activity by making a
forward pass through the network. The earliest finish time for the last
activity in the project identifies the total time required to complete the
project.
Step 6. Use the project completion time identified in step 5 as the latest finish
time for the last activity and make a backward pass through the network
to identify the latest start and latest finish time for each activity.
Step 7. Use the difference between the latest start time and the earliest start time
for each activity to determine the slack for each activity.
Step 8. Find the activities with zero slack; these are the critical activities.
Step 9. Use the information from steps 5 and 6 to develop the activity schedule
for the project.
Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s). Editorial review has
deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.