Page 431 -
P. 431
ECONOMIC ORDER QUANTITY (EOQ) MODEL 411
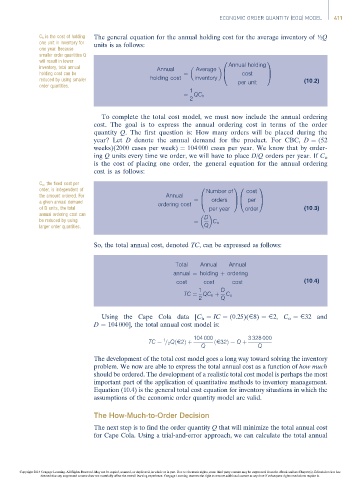
C h is the cost of holding The general equation for the annual holding cost for the average inventory of ½Q
one unit in inventory for units is as follows:
one year. Because
smaller order quantities Q
will result in lower 0 1
inventory, total annual Annual Average Annual holding
A
@
holding cost can be ¼ B cost C
reduced by using smaller holding cost inventory per unit (10:2)
order quantities.
1
¼ QC h
2
To complete the total cost model, we must now include the annual ordering
cost. The goal is to express the annual ordering cost in terms of the order
quantity Q. The first question is: How many orders will be placed during the
year? Let D denote the annual demand for the product. For CBC, D ¼ (52
weeks)(2000 cases per week) ¼ 104 000 cases per year. We know that by order-
ing Q units every time we order, we will have to place D/Q orders per year. If C o
is the cost of placing one order, the general equation for the annual ordering
cost is as follows:
C o , the fixed cost per
order, is independent of 0 Number of 10 cost 1
the amount ordered. For Annual B CB C
a given annual demand ordering cost ¼ @ orders A@ per A
of D units, the total per year order (10:3)
annual ordering cost can
D
be reduced by using ¼ C o
larger order quantities. Q
So, the total annual cost, denoted TC, can be expressed as follows:
Total Annual Annual
annual ¼ holding þ ordering
cost cost cost (10:4)
1 D
TC ¼ QC h þ C o
2 Q
Using the Cape Cola data [C h ¼ IC ¼ (0.25)(E8) ¼ E2, C o ¼ E32 and
D ¼ 104 000], the total annual cost model is:
104 000 3 328 000
1
TC ¼ = 2 QðE2Þþ ðE32Þ¼ Q þ
Q Q
The development of the total cost model goes a long way toward solving the inventory
problem. We now are able to express the total annual cost as a function of how much
should be ordered. The development of a realistic total cost model is perhaps the most
important part of the application of quantitative methods to inventory management.
Equation (10.4) is the general total cost equation for inventory situations in which the
assumptions of the economic order quantity model are valid.
The How-Much-to-Order Decision
The next step is to find the order quantity Q that will minimize the total annual cost
for Cape Cola. Using a trial-and-error approach, we can calculate the total annual
Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s). Editorial review has
deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.