Page 568 -
P. 568
548 CHAPTER 13 DECISION ANALYSIS
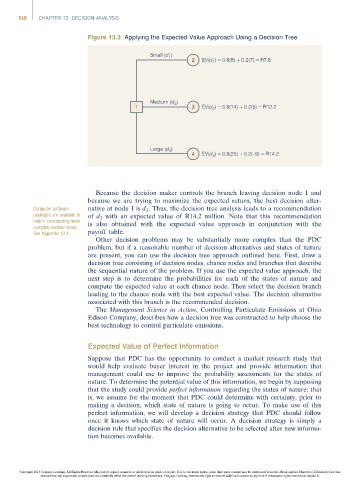
Figure 13.3 Applying the Expected Value Approach Using a Decision Tree
Small (d 1 )
2 EV(d ) = 0.8(8) + 0.2(7) = R7.8
1
Medium (d )
2
1 3 EV(d ) = 0.8(14) + 0.2(5) = R12.2
2
Large (d )
3
4 EV(d 3 ) = 0.8(20) + 0.2(–9) = R14.2
Because the decision maker controls the branch leaving decision node 1 and
because we are trying to maximize the expected return, the best decision alter-
Computer software native at node 1 is d 3 . Thus, the decision tree analysis leads to a recommendation
packages are available to of d 3 with an expected value of R14.2 million. Note that this recommendation
help in constructing more
complex decision trees. is also obtained with the expected value approach in conjunction with the
See Appendix 13.1. payoff table.
Other decision problems may be substantially more complex than the PDC
problem, but if a reasonable number of decision alternatives and states of nature
are present, you can use the decision tree approach outlined here. First, draw a
decision tree consisting of decision nodes, chance nodes and branches that describe
the sequential nature of the problem. If you use the expected value approach, the
next step is to determine the probabilities for each of the states of nature and
compute the expected value at each chance node. Then select the decision branch
leading to the chance node with the best expected value. The decision alternative
associated with this branch is the recommended decision.
The Management Science in Action, Controlling Particulate Emissions at Ohio
Edison Company, describes how a decision tree was constructed to help choose the
best technology to control particulate emissions.
Expected Value of Perfect Information
Suppose that PDC has the opportunity to conduct a market research study that
would help evaluate buyer interest in the project and provide information that
management could use to improve the probability assessments for the states of
nature. To determine the potential value of this information, we begin by supposing
that the study could provide perfect information regarding the states of nature; that
is, we assume for the moment that PDC could determine with certainty, prior to
making a decision, which state of nature is going to occur. To make use of this
perfect information, we will develop a decision strategy that PDC should follow
once it knows which state of nature will occur. A decision strategy is simply a
decision rule that specifies the decision alternative to be selected after new informa-
tion becomes available.
Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s). Editorial review has
deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.