Page 115 - An Introduction to Microelectromechanical Systems Engineering
P. 115
94 MEM Structures and Systems in Industrial and Automotive Applications
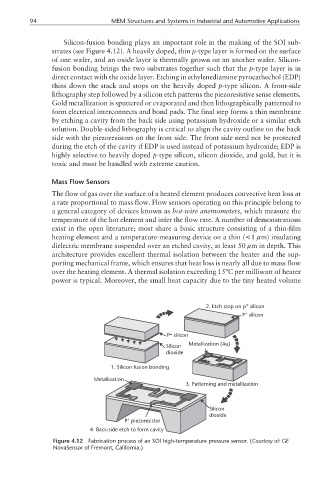
Silicon-fusion bonding plays an important role in the making of the SOI sub-
strates (see Figure 4.12). A heavily doped, thin p-type layer is formed on the surface
of one wafer, and an oxide layer is thermally grown on an another wafer. Silicon-
fusion bonding brings the two substrates together such that the p-type layer is in
direct contact with the oxide layer. Etching in ethylenediamine pyrocathechol (EDP)
thins down the stack and stops on the heavily doped p-type silicon. A front-side
lithography step followed by a silicon etch patterns the piezoresistive sense elements.
Gold metallization is sputtered or evaporated and then lithographically patterned to
form electrical interconnects and bond pads. The final step forms a thin membrane
by etching a cavity from the back side using potassium hydroxide or a similar etch
solution. Double-sided lithography is critical to align the cavity outline on the back
side with the piezoresistors on the front side. The front side need not be protected
during the etch of the cavity if EDP is used instead of potassium hydroxide; EDP is
highly selective to heavily doped p-type silicon, silicon dioxide, and gold, but it is
toxic and must be handled with extreme caution.
Mass Flow Sensors
The flow of gas over the surface of a heated element produces convective heat loss at
a rate proportional to mass flow. Flow sensors operating on this principle belong to
a general category of devices known as hot-wire anemometers, which measure the
temperature of the hot element and infer the flow rate. A number of demonstrations
exist in the open literature; most share a basic structure consisting of a thin-film
heating element and a temperature-measuring device on a thin (<1 µm) insulating
dielectric membrane suspended over an etched cavity, at least 50 µm in depth. This
architecture provides excellent thermal isolation between the heater and the sup-
porting mechanical frame, which ensures that heat loss is nearly all due to mass flow
over the heating element. A thermal isolation exceeding 15ºC per milliwatt of heater
power is typical. Moreover, the small heat capacity due to the tiny heated volume
+
2. Etch stop on p silicon
+
P silicon
+
P silicon
Metallization (Au)
Silicon
dioxide
1. Silicon fusion bonding
Metallization
3. Patterning and metallization
Silicon
dioxide
+
P piezoresistor
4. Back-side etch to form cavity
Figure 4.12 Fabrication process of an SOI high-temperature pressure sensor. (Courtesy of: GE
NovaSensor of Fremont, California.)