Page 26 - Analog and Digital Filter Design
P. 26
Introduction 23
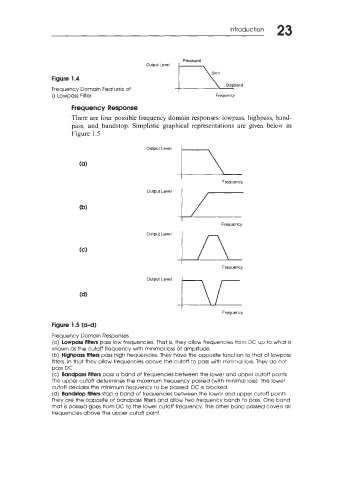
Passband
Output Level
Figure 1.4
-\ Sopband
Frequency Domain Features of
a Lowpass Filter Frequency
Frequency Response
There are four possible frequency domain responses: lowpass, highpass, band-
pass, and bandstop. Simplistic graphical representations are given below in
Figure 1.5
Frequency
Frequency
Frequency
Frequency
Figure 1.5 (a-d)
Frequency Domain Responses
(a) Lowpass filters pass low frequencies. That is, they allow frequencies from DC up to what is
known as the cutoff frequency with minimal loss of amplitude.
(b) Highpass filters pass high frequencies. They have the opposite function to that of lowpass
filters, in that they allow frequencies above the cutoff to pass with minimal loss. They do not
pass DC
(c) Bandpass filters pass a band of frequencies between the lower and upper cutoff points
The upper cutoff determines the maximum frequency passed (with minimal loss). The lower
cutoff decides the minimum frequency to be passed; DC is blocked.
(d) Bandstop filters stop a band of frequencies between the lower and upper cutoff points.
They are the opposite of bandpass filters and allow two frequency bands to pass. One band
that is passed goes from DC to the lower cutoff frequency. The other band passed covers all
frequencies above the upper cutoff point.