Page 267 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 267
6.17 HIGHER-VALENT TELLURIUM: A MECHANISTIC PUZZLE 247
OH
NO 2
P
Bu Bu Bu Se
H +
THF
Se NO 2
CN H
NO 2
+
Se
H 2 O 2 −
O
H
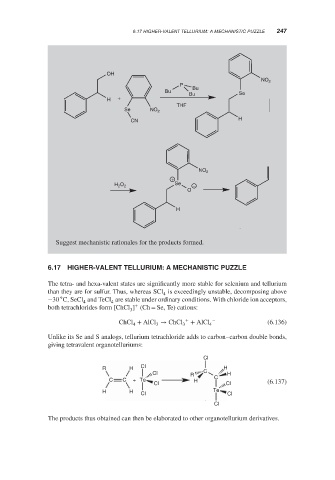
Suggest mechanistic rationales for the products formed.
6.17 HIGHER-VALENT TELLURIUM: A MECHANISTIC PUZZLE
The tetra- and hexa-valent states are significantly more stable for selenium and tellurium
than they are for sulfur. Thus, whereas SCl is exceedingly unstable, decomposing above
4
∘
−30 C, SeCl and TeCl are stable under ordinary conditions. With chloride ion acceptors,
4 4
+
both tetrachlorides form [ChCl ] (Ch = Se, Te) cations:
3
+ −
ChCl + AlCl → ChCl + AlCl (6.136)
4 3 3 4
Unlike its Se and S analogs, tellurium tetrachloride adds to carbon–carbon double bonds,
giving tetravalent organotelluriums:
Cl
R H Cl H
Cl R C H
C C + Te H C
Cl Cl (6.137)
H H Cl Te Cl
Cl
The products thus obtained can then be elaborated to other organotellurium derivatives.