Page 281 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 281
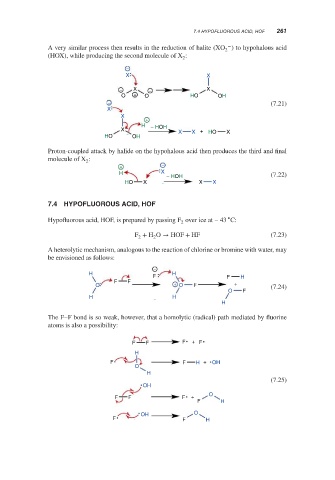
7.4 HYPOFLUOROUS ACID, HOF 261
−
A very similar process then results in the reduction of halite (XO ) to hypohalous acid
2
(HOX), while producing the second molecule of X :
2
−
X X
− X − X
O + O HO OH
− (7.21)
X
X
+
H − HOH
X X X + HO X
HO OH
Proton-coupled attack by halide on the hypohalous acid then produces the third and final
molecule of X :
2
+ −
H X
− HOH (7.22)
HO X X X
HYPOFLUOROUS ACID, HOF
7.4
∘
Hypofluorous acid, HOF, is prepared by passing F over ice at – 43 C:
2
F + H O → HOF + HF (7.23)
2 2
A heterolytic mechanism, analogous to the reaction of chlorine or bromine with water, may
be envisioned as follows:
−
H H
F F H
F F
O + O F + (7.24)
O F
H H
H
The F–F bond is so weak, however, that a homolytic (radical) path mediated by fluorine
atoms is also a possibility:
F F F + F
H
F F H + OH
O
H
(7.25)
OH
O
F F F +
F H
OH O
F F H