Page 284 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 284
THE HALOGENS
264
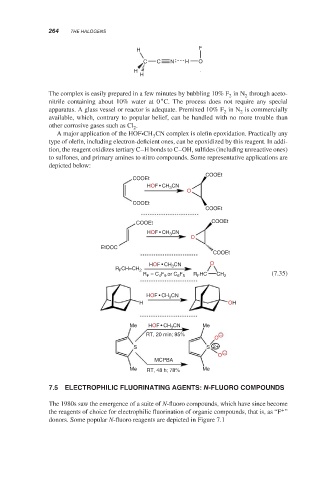
H F
C C N H O
H
H
The complex is easily prepared in a few minutes by bubbling 10% F in N through aceto-
2
2
∘
nitrile containing about 10% water at 0 C. The process does not require any special
apparatus. A glass vessel or reactor is adequate. Premixed 10% F in N is commercially
2 2
available, which, contrary to popular belief, can be handled with no more trouble than
other corrosive gases such as Cl .
2
A major application of the HOF •CH CN complex is olefin epoxidation. Practically any
3
type of olefin, including electron-deficient ones, can be epoxidized by this reagent. In addi-
tion, the reagent oxidizes tertiary C–H bonds to C–OH, sulfides (including unreactive ones)
to sulfones, and primary amines to nitro compounds. Some representative applications are
depicted below:
COOEt
COOEt
HOF•CH 3 CN
O
COOEt
COOEt
COOEt COOEt
HOF•CH 3 CN
O
EtOOC
COOEt
HOF•CH 3 CN O
R F CH=CH 2
R F = C 4 F 9 or C 6 F 5 R F HC CH 2 (7.35)
HOF•CH 3 CN
H OH
Me HOF•CH 3 CN Me
RT, 20 min; 95% −
O
S S 2+
−
O
MCPBA
Me RT, 48 h; 78% Me
7.5 ELECTROPHILIC FLUORINATING AGENTS: N-FLUORO COMPOUNDS
The 1980s saw the emergence of a suite of N-fluoro compounds, which have since become
+
the reagents of choice for electrophilic fluorination of organic compounds, that is, as “F ”
donors. Some popular N-fluoro reagents are depicted in Figure 7.1