Page 285 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 285
7.5 ELECTROPHILIC FLUORINATING AGENTS: N-FLUORO COMPOUNDS 265
−
O −
O
F 3 C S 2+
N F −
N CF SO 3
3
+
C
F 3 S 2+
− F
O
O
−
(a) (b)
− −
O O
S 2+ Cl
N −
N F +
BF 4
N
S 2+ +
−
F BF
− O O − 4
(c) (d)
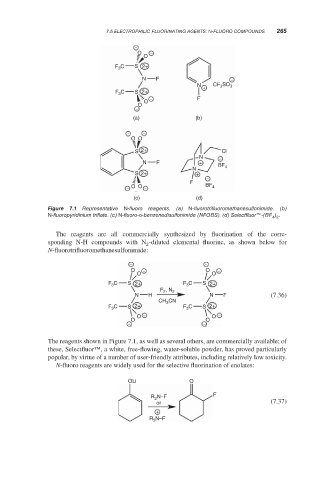
7.1 Representative N-fluoro reagents. (a) N-fluorotrifluoromethanesulfonimide. (b)
Figure
N-fluoropyridinium triflate. (c) N-fluoro-o-benzenedisulfonimide (NFOBS). (d) Selectfluor™-(BF ) .
4 2
The reagents are all commercially synthesized by fluorination of the corre-
sponding N-H compounds with N -diluted elemental fluorine, as shown below for
2
N-fluorotrifluoromethanesulfonimide:
− −
O − O −
O O
F C S 2+ F 3 C S 2+
3
F , N 2
2
N H N F (7.36)
CH CN
3
C F 3 C
F 3 S 2+ S 2+
O − O −
O O
− −
The reagents shown in Figure 7.1, as well as several others, are commercially available; of
these, Selectfluor™, a white, free-flowing, water-soluble powder, has proved particularly
popular, by virtue of a number of user-friendly attributes, including relatively low toxicity.
N-fluoro reagents are widely used for the selective fluorination of enolates:
OLi O
R 2 N–F F
or (7.37)
+
R 3 N–F