Page 297 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 297
7.9 HALOGENS IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS: SOME CLASSICAL REACTIONS 277
mechanism accounts for the stereospecificity of the process, which may be described as an
anti addition; that is, the two bromine atoms add to opposite faces of the double bond. It’s
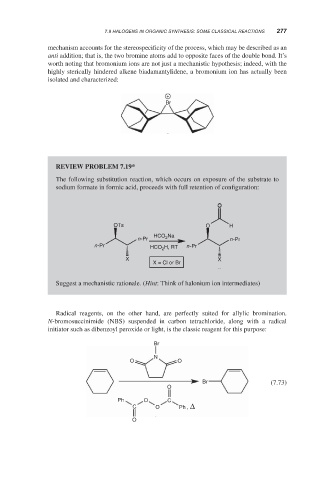
worth noting that bromonium ions are not just a mechanistic hypothesis; indeed, with the
highly sterically hindered alkene biadamantylidene, a bromonium ion has actually been
isolated and characterized:
+
Br
REVIEW PROBLEM 7.19*
The following substitution reaction, which occurs on exposure of the substrate to
sodium formate in formic acid, proceeds with full retention of configuration:
O O
OTs O H
Na
HCO 2
n-Pr n-Pr
n-Pr HCO H, RT n-Pr
2
X X
X = Cl or Br
Suggest a mechanistic rationale. (Hint: Think of halonium ion intermediates)
Radical reagents, on the other hand, are perfectly suited for allylic bromination.
N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) suspended in carbon tetrachloride, along with a radical
initiator such as dibenzoyl peroxide or light, is the classic reagent for this purpose:
Br
N
O O
Br (7.73)
O
Ph O C
C O Ph , Δ
O