Page 299 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 299
7.9 HALOGENS IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS: SOME CLASSICAL REACTIONS 279
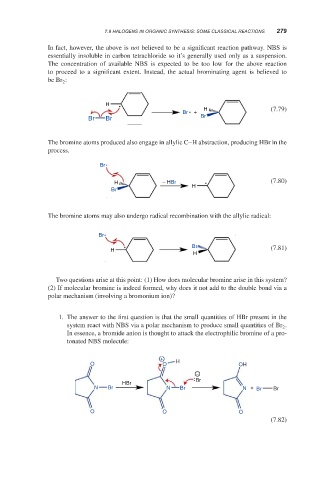
In fact, however, the above is not believed to be a significant reaction pathway. NBS is
essentially insoluble in carbon tetrachloride so it’s generally used only as a suspension.
The concentration of available NBS is expected to be too low for the above reaction
to proceed to a significant extent. Instead, the actual brominating agent is believed to
be Br :
2
H
H (7.79)
Br +
Br Br Br
The bromine atoms produced also engage in allylic C–H abstraction, producing HBr in the
process.
Br
H − HBr (7.80)
H
Br
The bromine atoms may also undergo radical recombination with the allylic radical:
Br
Br
H (7.81)
H
Two questions arise at this point: (1) How does molecular bromine arise in this system?
(2) If molecular bromine is indeed formed, why does it not add to the double bond via a
polar mechanism (involving a bromonium ion)?
1. The answer to the first question is that the small quantities of HBr present in the
system react with NBS via a polar mechanism to produce small quantities of Br .
2
In essence, a bromide anion is thought to attack the electrophilic bromine of a pro-
tonated NBS molecule:
+
O O H OH
−
Br
HBr
N Br N Br N + Br Br
O O O
(7.82)