Page 87 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 87
3.1 GROUP 13 COMPOUNDS AS LEWIS ACIDS 67
• Like beryllium and magnesium halides, aluminum and gallium halides undergo partial
hydrolysis in aqueous solutions, resulting in acidic solutions.
• To satisfy their hunger for electron pairs, many of the trivalent compounds exist as
dimers such as diborane (B H ) and Al Cl .
2
6
2
6
+
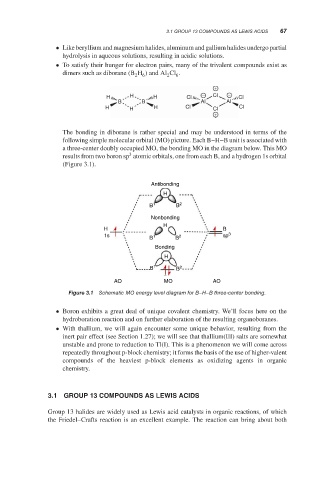
H H H Cl − Cl − Cl
B B Al Al
H H H Cl Cl Cl
+
The bonding in diborane is rather special and may be understood in terms of the
following simple molecular orbital (MO) picture. Each B–H–B unit is associated with
a three-center doubly occupied MO, the bonding MO in the diagram below. This MO
3
results from two boron sp atomic orbitals, one from each B, and a hydrogen 1s orbital
(Figure 3.1).
Antibonding
H
B 1 B 2
Nonbonding
H
H B
1s 1 2 sp 3
B B
Bonding
H
B 1 B 2
AO MO AO
Schematic MO energy level diagram for B–H–B three-center bonding.
Figure 3.1
• Boron exhibits a great deal of unique covalent chemistry. We’ll focus here on the
hydroboration reaction and on further elaboration of the resulting organoboranes.
• With thallium, we will again encounter some unique behavior, resulting from the
inert pair effect (see Section 1.27); we will see that thallium(III) salts are somewhat
unstable and prone to reduction to Tl(I). This is a phenomenon we will come across
repeatedly throughout p-block chemistry; it forms the basis of the use of higher-valent
compounds of the heaviest p-block elements as oxidizing agents in organic
chemistry.
3.1 GROUP 13 COMPOUNDS AS LEWIS ACIDS
Group 13 halides are widely used as Lewis acid catalysts in organic reactions, of which
the Friedel–Crafts reaction is an excellent example. The reaction can bring about both