Page 92 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 92
GROUP 13 ELEMENTS
72
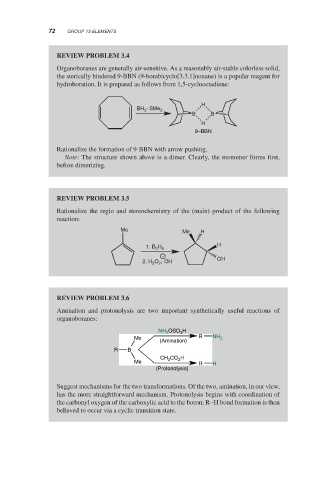
REVIEW PROBLEM 3.4
Organoboranes are generally air-sensitive. As a reasonably air-stable colorless solid,
the sterically hindered 9-BBN (9-borabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane) is a popular reagent for
hydroboration. It is prepared as follows from 1,5-cyclooctadiene:
H
BH 3 ∙SMe 2
B B
H
9–BBN
Rationalize the formation of 9-BBN with arrow pushing.
Note: The structure shown above is a dimer. Clearly, the monomer forms first,
before dimerizing.
REVIEW PROBLEM 3.5
Rationalize the regio and stereochemistry of the (main) product of the following
reaction:
Me Me H
H
2
1. B H 6
−
2. H 2 O 2 ,OH OH
REVIEW PROBLEM 3.6
Amination and protonolysis are two important synthetically useful reactions of
organoboranes:
OSO H
NH 2 3
Me R NH 2
(Amination)
R B
CH CO H
Me 3 2 R H
(Protonolysis)
Suggest mechanisms for the two transformations. Of the two, amination, in our view,
has the more straightforward mechanism. Protonolysis begins with coordination of
the carbonyl oxygen of the carboxylic acid to the boron; R–H bond formation is then
believed to occur via a cyclic transition state.