Page 89 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 89
3.1 GROUP 13 COMPOUNDS AS LEWIS ACIDS 69
REVIEW PROBLEM 3.2
Aluminum halides are used to prepare CBr or CI via halide exchange from CCl ,
4 4 4
as shown below:
(a) 3 CCl + 4 AlBr 3 3 CBr + 4 AlCl 3
4
4
AlCl 3
(b) CCl 4 + 4 C 2 H 5 I Cl 4 + 4 C 2 H 5 Cl
Suggest mechanisms for the two transformations. Note:In(a),AlBr is a stoichio-
3
metric reagent. In (b), AlCl is a catalyst.
3
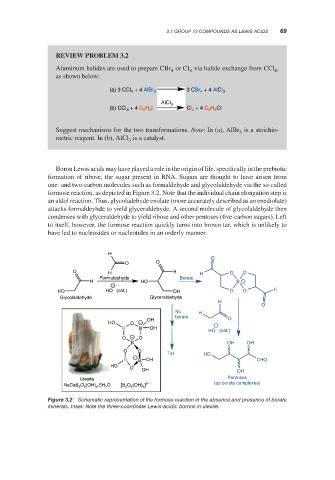
Boron Lewis acids may have played a role in the origin of life, specifically in the prebiotic
formation of ribose, the sugar present in RNA. Sugars are thought to have arisen from
one- and two-carbon molecules such as formaldehyde and glycolaldehyde via the so-called
formose reaction, as depicted in Figure 3.2. Note that the individual chain elongation step is
an aldol reaction. Thus, glycoladehyde enolate (more accurately described as an enediolate)
attacks formaldeyhde to yield glyceraldehyde. A second molecule of glycolaldehyde then
condenses with glyceraldehyde to yield ribose and other pentoses (five-carbon sugars). Left
to itself, however, the formose reaction quickly turns into brown tar, which is unlikely to
have led to nucleosides or nucleotides in an orderly manner.
H
O
O O
O H H H O O
Formaldehyde Borate
H HO B −
−
HO HO (cat.) OH O O H
Glycolaldehyde Glyceraldehyde
H
O
No H
borate
OH O ,
HO O − −
B B OH
HO (cat.)
O − O
B OH OH
O O
Tar HO
−
B B OH CHO
HO
O
OH OH
Ulexite Pentoses
3− (as borate complexes)
NaCaB O (OH) .5H O [B O (OH) ]
6
5
6
6
5
2
6
Figure 3.2 Schematic representation of the formose reaction in the absence and presence of borate
minerals. Inset: Note the three-coordinate Lewis-acidic borons in ulexite.