Page 133 - Artificial Intelligence for Computational Modeling of the Heart
P. 133
Chapter 3 Learning cardiac anatomy 105
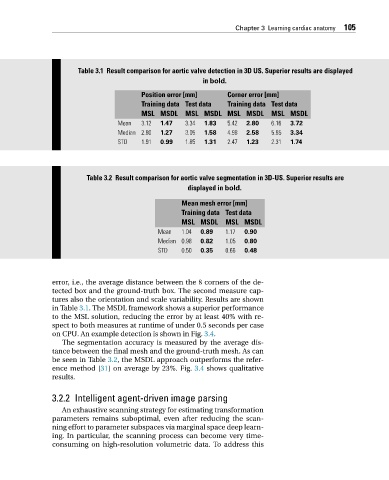
Table 3.1 Result comparison for aortic valve detection in 3D US. Superior results are displayed
in bold.
Position error [mm] Corner error [mm]
Training data Test data Training data Test data
MSL MSDL MSL MSDL MSL MSDL MSL MSDL
Mean 3.12 1.47 3.34 1.83 5.42 2.80 6.16 3.72
Median 2.80 1.27 3.05 1.58 4.98 2.58 5.85 3.34
STD 1.91 0.99 1.85 1.31 2.47 1.23 2.31 1.74
Table 3.2 Result comparison for aortic valve segmentation in 3D-US. Superior results are
displayed in bold.
Mean mesh error [mm]
Training data Test data
MSL MSDL MSL MSDL
Mean 1.04 0.89 1.17 0.90
Median 0.98 0.82 1.05 0.80
STD 0.50 0.35 0.66 0.48
error, i.e., the average distance between the 8 corners of the de-
tected box and the ground-truth box. The second measure cap-
tures also the orientation and scale variability. Results are shown
in Table 3.1. The MSDL framework shows a superior performance
to the MSL solution, reducing the error by at least 40% with re-
spect to both measures at runtime of under 0.5 seconds per case
on CPU. An example detection is shown in Fig. 3.4.
The segmentation accuracy is measured by the average dis-
tance between the final mesh and the ground-truth mesh. As can
be seen in Table 3.2, the MSDL approach outperforms the refer-
ence method [31] on average by 23%. Fig. 3.4 shows qualitative
results.
3.2.2 Intelligent agent-driven image parsing
An exhaustive scanning strategy for estimating transformation
parameters remains suboptimal, even after reducing the scan-
ning effort to parameter subspaces via marginal space deep learn-
ing. In particular, the scanning process can become very time-
consuming on high-resolution volumetric data. To address this