Page 175 - Artificial Intelligence for Computational Modeling of the Heart
P. 175
Chapter 4 Data-driven reduction of cardiac models 147
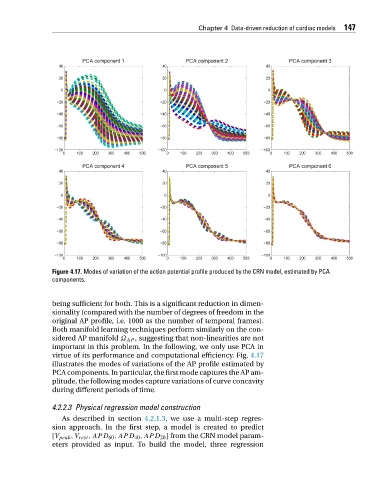
Figure 4.17. Modes of variation of the action potential profile produced by the CRN model, estimated by PCA
components.
being sufficient for both. This is a significant reduction in dimen-
sionality (compared with the number of degrees of freedom in the
original AP profile, i.e. 1000 as the number of temporal frames).
Both manifold learning techniques perform similarly on the con-
sidered AP manifold Ω AP , suggesting that non-linearities are not
important in this problem. In the following, we only use PCA in
virtue of its performance and computational efficiency. Fig. 4.17
illustrates the modes of variations of the AP profile estimated by
PCA components. In particular, the first mode captures the AP am-
plitude, the following modes capture variations of curve concavity
during different periods of time.
4.2.2.3 Physical regression model construction
As described in section 4.2.1.3, we use a multi-step regres-
sion approach. In the first step, a model is created to predict
[V peak ,V rest ,APD 60 ,APD 40 ,APD 20 ] from the CRN model param-
eters provided as input. To build the model, three regression