Page 32 - Automotive Engineering Powertrain Chassis System and Vehicle Body
P. 32
CH AP TER 2 .1 Measurement of torque, power, speed and fuel consumption
9
2
1
4
5
6
7
8
3
10
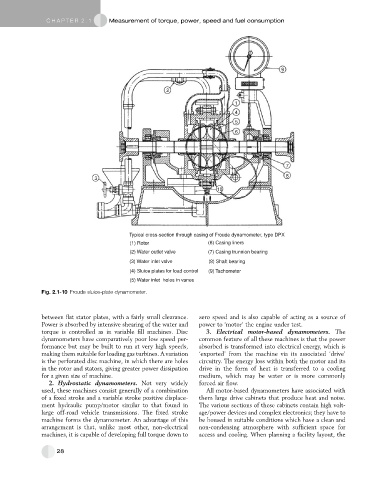
Typical cross-section through casing of Froude dynamometer, type DPX
(1) Rotor (6) Casing liners
(2) Water outlet valve (7) Casing trunnion bearing
(3) Water inlet valve (8) Shaft bearing
(4) Sluice plates for load control (9) Tachometer
(5) Water inlet holes in vanes
Fig. 2.1-10 Froude sluice-plate dynamometer.
between flat stator plates, with a fairly small clearance. zero speed and is also capable of acting as a source of
Power is absorbed by intensive shearing of the water and power to ‘motor’ the engine under test.
torque is controlled as in variable fill machines. Disc 3. Electrical motor-based dynamometers. The
dynamometers have comparatively poor low speed per- common feature of all these machines is that the power
formance but may be built to run at very high speeds, absorbed is transformed into electrical energy, which is
making them suitable for loading gas turbines. A variation ‘exported’ from the machine via its associated ‘drive’
is the perforated disc machine, in which there are holes circuitry. The energy loss within both the motor and its
in the rotor and stators, giving greater power dissipation drive in the form of heat is transferred to a cooling
for a given size of machine. medium, which may be water or is more commonly
2. Hydrostatic dynamometers. Not very widely forced air flow.
used, these machines consist generally of a combination All motor-based dynamometers have associated with
of a fixed stroke and a variable stroke positive displace- them large drive cabinets that produce heat and noise.
ment hydraulic pump/motor similar to that found in The various sections of these cabinets contain high volt-
large off-road vehicle transmissions. The fixed stroke age/power devices and complex electronics; they have to
machine forms the dynamometer. An advantage of this be housed in suitable conditions which have a clean and
arrangement is that, unlike most other, non-electrical non-condensing atmosphere with sufficient space for
machines, it is capable of developing full torque down to access and cooling. When planning a facility layout, the
28