Page 541 - Automotive Engineering Powertrain Chassis System and Vehicle Body
P. 541
CHAP TER 1 6. 2 Standard sedan (saloon) – baseline load paths
Q 3
Q X1 L 7 h 4
R
Q 1 RT
Q 2 Q 4 Q 1 Q 5
h 3 R RT
Q 3 Q 1 P Q 5
Q 4 RT Q 1
Q X2
Q 4 Q1
Q X1 Q Q 6
Q 3 Q T
h 1 P 1 5
Q 2 Q 1 FT P FT Q 3 Q X1 Q X2 Q 6 Q 6 h
R FT Q 1 2
P FT T R FT Q X1 Q B
Q 2 7 S R
R FT Q 1 Q Q Q
R FT P FT 2 7 1
P FT P RT
R FT P FT P RT
R FT P FT P FT
Q 1 Q 7
L
S F 5
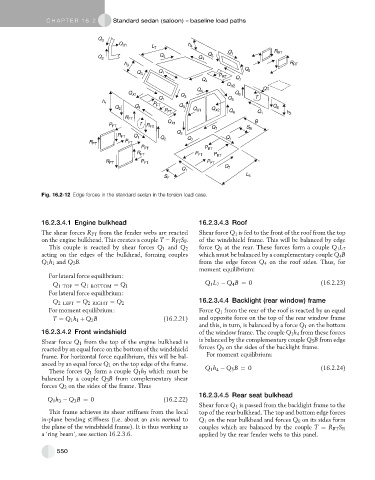
Fig. 16.2-12 Edge forces in the standard sedan in the torsion load case.
16.2.3.4.1 Engine bulkhead 16.2.3.4.3 Roof
The shear forces R FT from the fender webs are reacted Shear force Q 1 is fed to the front of the roof from the top
on the engine bulkhead. This creates a couple T ¼ R FT S F . of the windshield frame. This will be balanced by edge
This couple is reacted by shear forces Q 1 and Q 2 force Q 1 at the rear. These forces form a couple Q 1 L 7
acting on the edges of the bulkhead, forming couples which must be balanced by a complementary couple Q 4 B
Q 1 h 1 and Q 2 B. from the edge forces Q 4 on the roof sides. Thus, for
moment equilibrium:
For lateral force equilibrium:
Q 1 L 7 Q B ¼ 0 (16.2.23)
Q 1 TOP ¼ Q 1 BOTTOM ¼ Q 1 4
For lateral force equilibrium:
16.2.3.4.4 Backlight (rear window) frame
Q 2 LEFT ¼ Q 2 RIGHT ¼ Q 2
For moment equilibrium: Force Q 1 from the rear of the roof is reacted by an equal
T ¼ Q 1 h 1 þ Q 2 B (16.2.21) and opposite force on the top of the rear window frame
and this, in turn, is balanced by a force Q 1 on the bottom
16.2.3.4.2 Front windshield of the window frame. The couple Q 1 h 4 from these forces
Shear force Q 1 from the top of the engine bulkhead is is balanced by the complementary couple Q 5 B from edge
reacted by an equal force on the bottom of the windshield forces Q 5 on the sides of the backlight frame.
frame. For horizontal force equilibrium, this will be bal- For moment equilibrium:
anced by an equal force Q 1 on the top edge of the frame.
4
These forces Q 1 form a couple Q 1 h 3 which must be Q 1 h Q 5 B ¼ 0 (16.2.24)
balanced by a couple Q 3 B from complementary shear
forces Q 3 on the sides of the frame. Thus
16.2.3.4.5 Rear seat bulkhead
Q 1 h 3 Q 3 B ¼ 0 (16.2.22)
Shear force Q 1 is passed from the backlight frame to the
This frame achieves its shear stiffness from the local top of the rear bulkhead. The top and bottom edge forces
in-plane bending stiffness (i.e. about an axis normal to Q 1 on the rear bulkhead and forces Q 6 on its sides form
the plane of the windshield frame). It is thus working as couples which are balanced by the couple T ¼ R RT S R
a ‘ring beam’, see section 16.2.3.6. applied by the rear fender webs to this panel.
550