Page 209 - Bebop to The Boolean Boogie An Unconventional Guide to Electronics Fundamentals, Components, and Processes
P. 209
7 90 Chapter Sixteen
/
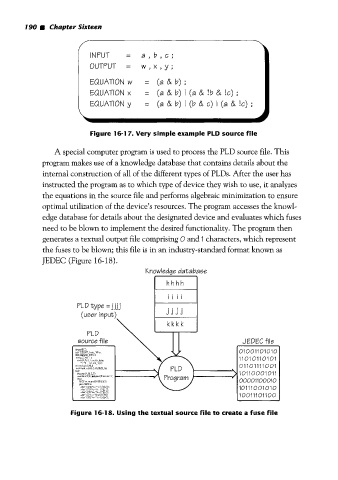
INPUT = a, b, G;
OUTPUT = w , x , y ;
EQUATION w = (a & b) ;
EQUATION x = (a & b) I (a & !b & !G) ;
EQUATION y = (a & b) I (b & G) I (a & !G) ;
Figure 16-1 7. Very simple example PLD source file
A special computer program is used to process the PLD source file. This
program makes use of a knowledge database that contains details about the
internal construction of all of the different types of PLDs. After the user has
instructed the program as to which type of device they wish to use, it analyzes
the equations in the source file and performs algebraic minimization to ensure
optimal utilization of the device’s resources. The program accesses the knowl-
edge database for details about the designated device and evaluates which fuses
need to be blown to implement the desired functionality. The program then
generates a textual output file comprising O and I characters, which represent
the fuses to be blown; this file is in an industry-standard format known as
JEDEC (Figure 16-1 8).
Knowledqe database
11 01 01 101 01
01101111001
10110001011
00001100010
Figure 16-18. Using the textual source file to create a fuse file