Page 355 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 355
15.3 Cascade Reactions for Assaying Transketolase Activity by In Vivo Selection 331
100
90
80
70
D-S7P (a.u.) 50
60
40
30
20
10
0
0 2 4 6 8
Time (h)
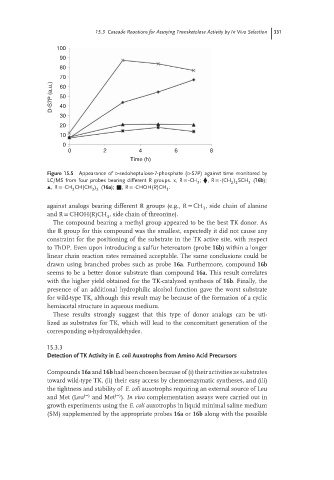
Figure 15.5 Appearance of D-sedoheptulose-7-phosphate (D-S7P) against time monitored by
LC/MS from four probes bearing different R groups. x, R = -CH ; ⧫,R = -(CH ) SCH (16b);
3
3
2 2
▴,R = -CH CH(CH ) (16a); ■,R = -CHOH(R)CH .
2
3 2
3
against analogs bearing different R groups (e.g., R = CH , side chain of alanine
3
and R = CHOH(R)CH , side chain of threonine).
3
The compound bearing a methyl group appeared to be the best TK donor. As
the R group for this compound was the smallest, expectedly it did not cause any
constraint for the positioning of the substrate in the TK active site, with respect
to ThDP. Even upon introducing a sulfur heteroatom (probe 16b)withinalonger
linear chain reaction rates remained acceptable. The same conclusions could be
drawn using branched probes such as probe 16a. Furthermore, compound 16b
seems to be a better donor substrate than compound 16a. This result correlates
with the higher yield obtained for the TK-catalyzed synthesis of 16b.Finally,the
presence of an additional hydrophilic alcohol function gave the worst substrate
for wild-type TK, although this result may be because of the formation of a cyclic
hemiacetal structure in aqueous medium.
These results strongly suggest that this type of donor analogs can be uti-
lized as substrates for TK, which will lead to the concomitant generation of the
corresponding α-hydroxyaldehydes.
15.3.3
Detection of TK Activity in E. coli Auxotrophs from Amino Acid Precursors
Compounds 16a and 16b had been chosen because of (i) their activities as substrates
toward wild-type TK, (ii) their easy access by chemoenzymatic syntheses, and (iii)
the tightness and stability of E. coli auxotrophs requiring an external source of Leu
(−)
and Met (Leu (−) and Met ). In vivo complementation assays were carried out in
growth experiments using the E. coli auxotrophs in liquid minimal saline medium
(SM) supplemented by the appropriate probes 16a or 16b along with the possible