Page 439 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 439
18.3 Conclusion and Outlook 415
CH 3 OH OH H C O
3
O O
H C HO
3
N
HO CH 3
N N
CH 3 H C
O 3 O O
CH 3 O CH 3
O
30 31 32
CH 3
O H 3 C O
O
O H C
3
CH HO
N 3
HO CH 3
N N
HO
H C
3
O O OH
CH 3
O O
CH CH 3
33 3 34 35
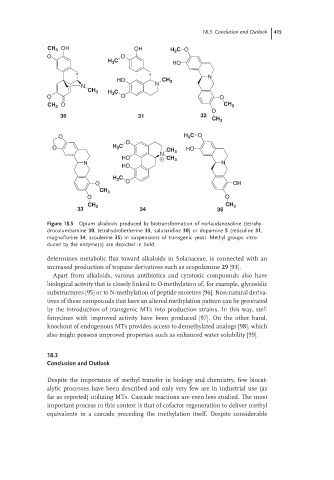
Figure 18.5 Opium alkaloids produced by biotransformation of norlaudanosoline (tetrahy-
drocolumbamine 30, tetrahydroberberine 33, salutaridine 30) or dopamine 5 (reticuline 31,
magnoflorine 34,scoulerine 35) in suspensions of transgenic yeast. Methyl groups intro-
duced by the enzyme(s) are depicted in bold.
determines metabolic flux toward alkaloids in Solanaceae, is connected with an
increased production of tropane derivatives such as scopolamine 29 [93].
Apart from alkaloids, various antibiotics and cytotoxic compounds also have
biological activity that is closely linked to O-methylation of, for example, glycosidic
substructures [95] or to N-methylation of peptide moieties [96]. Non-natural deriva-
tives of these compounds that have an altered methylation pattern can be generated
by the introduction of transgenic MTs into production strains. In this way, stef-
fimycines with improved activity have been produced [97]. On the other hand,
knockout of endogenous MTs provides access to demethylated analogs [98], which
also might possess improved properties such as enhanced water solubility [99].
18.3
Conclusion and Outlook
Despite the importance of methyl transfer in biology and chemistry, few biocat-
alytic processes have been described and only very few are in industrial use (as
far as reported) utilizing MTs. Cascade reactions are even less studied. The most
important process in this context is that of cofactor regeneration to deliver methyl
equivalents in a cascade preceding the methylation itself. Despite considerable